Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2010; 16(28): 3529-3540
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3529
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3529
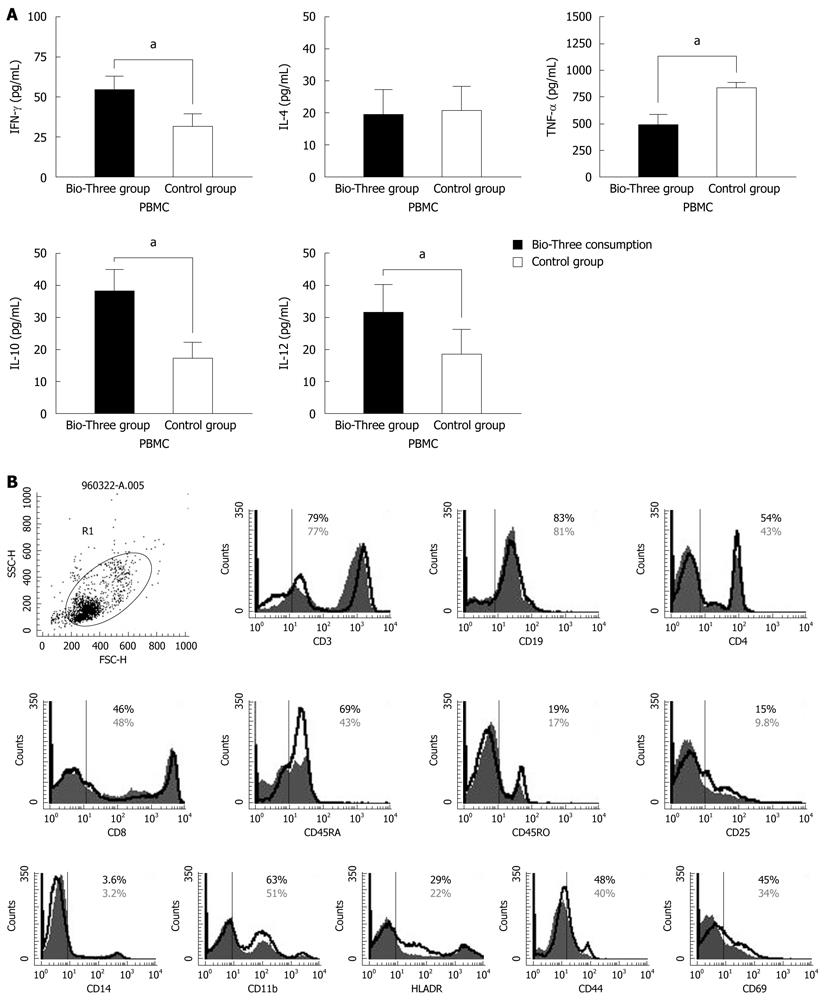
Figure 4 Measuring initial cytokine levels and determining immune phenotype distributions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from blood donors.
A: Initial concentrations of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin (IL)-4, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-10, and IL-12 p70 in the supernatants of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The results are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistically significant differences compared with the controls (aP < 0.05); B: To determine the effect of Bio-Three on PBMCs, phenotypic analysis of the immune response was studied. The solid histogram shows the control results, and the unshaded area shows the level of expression of co-stimulatory molecules after Bio-Three consumption. The data shown are representative of three experiments performed. Probiotics might enhance expression of CD4, CD45RB, CD44, CD69, CD25, CD11b and HLA-DR, which indicates alternation of co-stimulatory markers of T helper cells and dendritic cells.
- Citation: Hua MC, Lin TY, Lai MW, Kong MS, Chang HJ, Chen CC. Probiotic Bio-Three induces Th1 and anti-inflammatory effects in PBMC and dendritic cells. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(28): 3529-3540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i28/3529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3529