Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2010; 16(28): 3499-3509
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3499
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3499
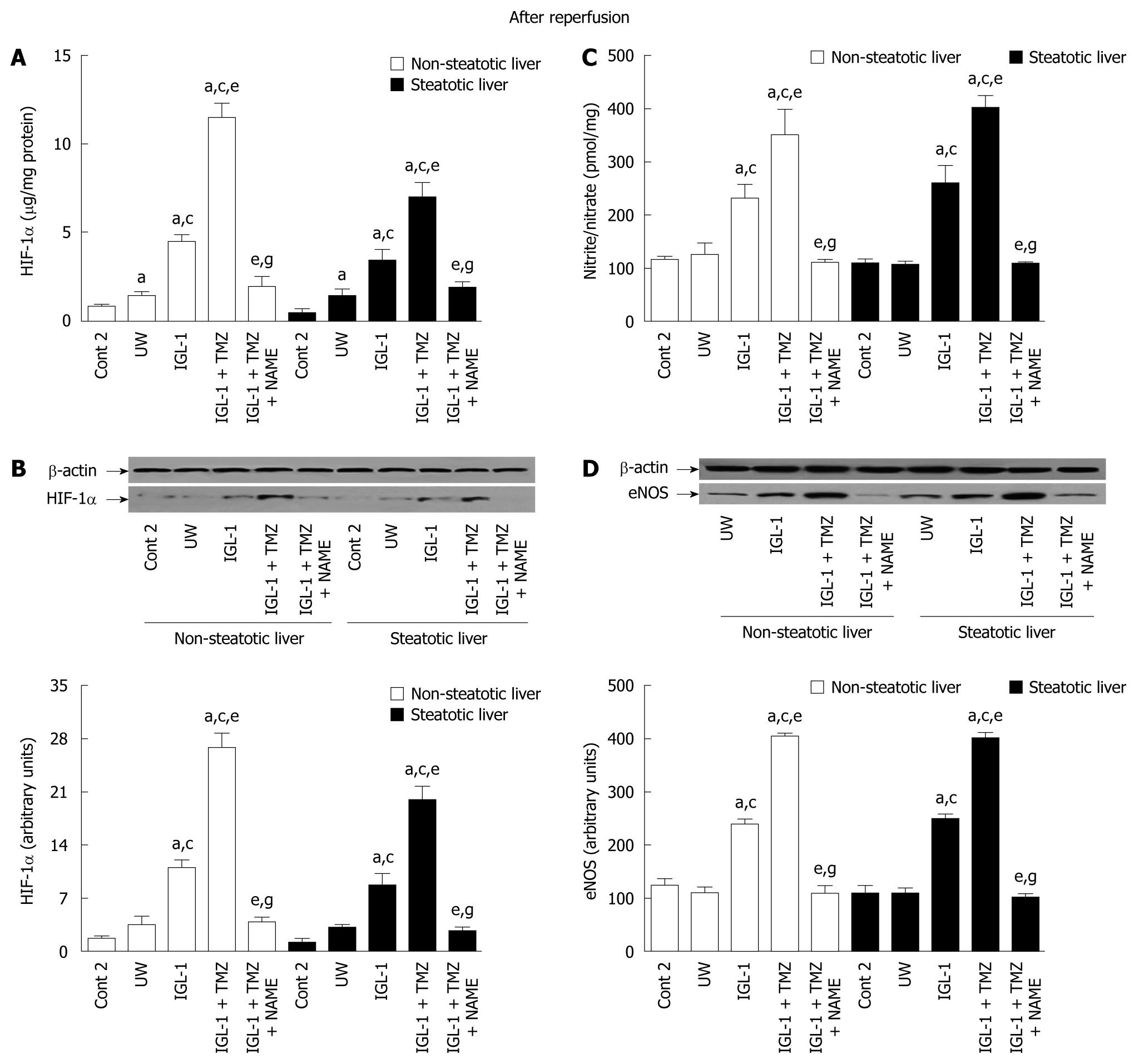
Figure 2 Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, nitrite/nitrate and endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
A: Hypoxia-induced factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein levels quantified by Trans AM HIF-1α kit after 24 h of cold storage and 120 min of normothermic reperfusion; B: Representative Western blotting of HIF-1α (top) and densitometric analysis (bottom) after 24 h of cold storage and 120 min of normothermic reperfusion; C: Nitrite/nitrate levels after 120 min of normothermic reperfusion; D: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) protein levels in liver after 120 min of normothermic reperfusion. Representative Western blotting (top) and densitometric analysis (bottom). Cont 2: Liver flushed and perfused ex vivo without cold preservation; University Wisconsin (UW): Liver preserved in UW solution; IGL-1 + trimetazidine (TMZ) + NAME: Liver preserved in IGL-1 solution with TMZ and an nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor, L-NAME. aP < 0.05 vs Cont 2; cP < 0.05 vs UW; eP < 0.05 vs IGL-1; gP < 0.05 vs IGL-1 + TMZ.
- Citation: Zaouali MA, Mosbah IB, Boncompagni E, Abdennebi HB, Mitjavila MT, Bartrons R, Freitas I, Rimola A, Roselló-Catafau J. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α accumulation in steatotic liver preservation: Role of nitric oxide. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(28): 3499-3509
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i28/3499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3499