Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2010; 16(27): 3411-3417
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3411
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3411
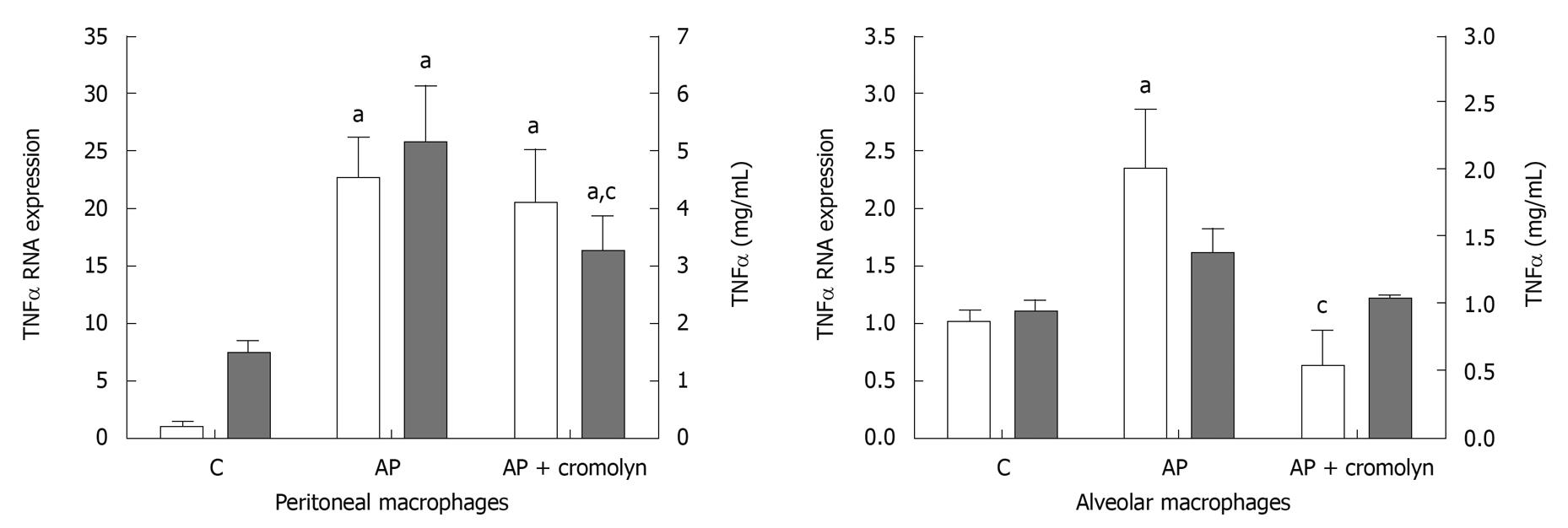
Figure 3 Both peritoneal and alveolar macrophages were activated after induction of pancreatitis, but the expression of tumor necrosis factor α mRNA in peritoneal macrophages was one order of magnitude higher than that observed in alveolar macrophages.
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α release was induced in peritoneal cells, while in alveolar cells the observed increase was not statistically significant. Cromolyn treatment completely prevented the activation of alveolar macrophages. In contrast, peritoneal macrophages remained activated under cromolyn treatment. aP < 0.05 vs C; cP < 0.05 vs AP. C: Control; AP: Acute pancreatitis.
- Citation: Lopez-Font I, Gea-Sorlí S, de-Madaria E, Gutiérrez LM, Pérez-Mateo M, Closa D. Pancreatic and pulmonary mast cells activation during experimental acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(27): 3411-3417
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i27/3411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3411