Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2010; 16(27): 3411-3417
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3411
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3411
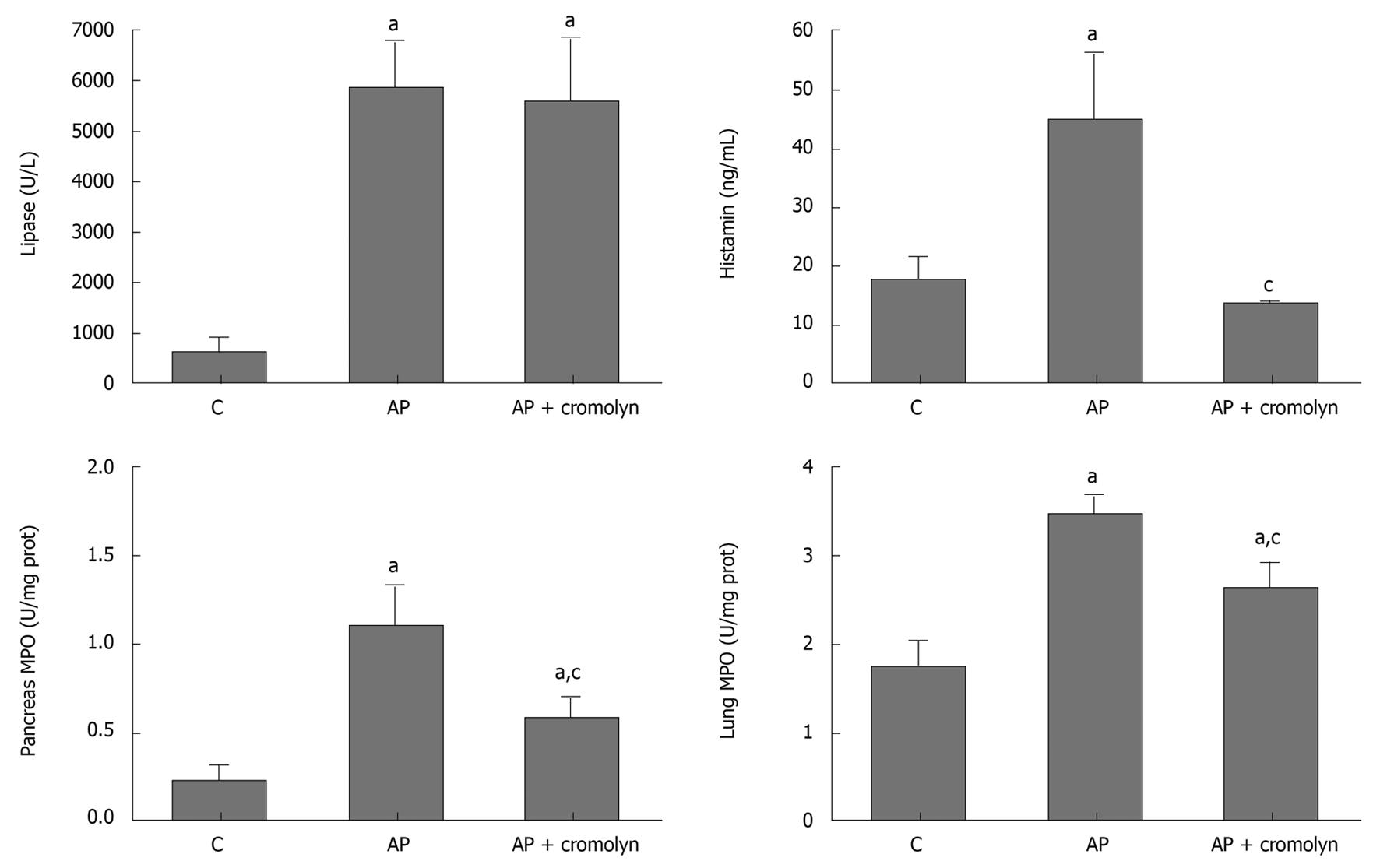
Figure 2 Effect of mast cell inhibitor, cromolyn.
Three hours after pancreatitis induction, increased levels of lipase and histamine were detected in plasma. Cromolyn treatment had no effect on lipase, which is related to acinar cell damage, but prevented the increase in histamine. In tissue, leukocyte infiltration was evaluated by measuring myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. Pancreatitis resulted in increased MPO activity in both pancreas and lung. Cromolyn treatment partially prevented these increases. aP < 0.05 vs C; cP < 0.05 vs AP. C: Control; AP: Acute pancreatitis.
- Citation: Lopez-Font I, Gea-Sorlí S, de-Madaria E, Gutiérrez LM, Pérez-Mateo M, Closa D. Pancreatic and pulmonary mast cells activation during experimental acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(27): 3411-3417
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i27/3411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3411