Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2010; 16(26): 3330-3334
Published online Jul 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i26.3330
Published online Jul 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i26.3330
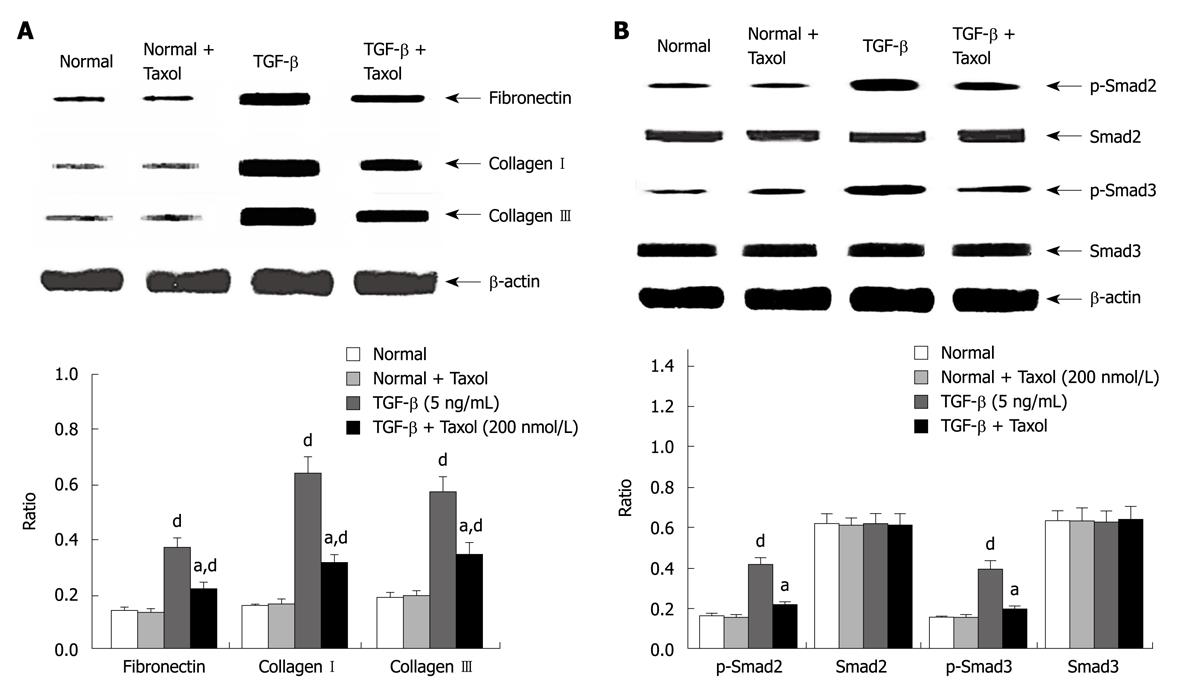
Figure 2 The protein levels changes in vitro after treatment.
A: Western blotting analyses depicting fibronectin and collagen I and III mRNA expression in vitro following paclitaxel treatment in HSCs. Whole hepatic cell extracts were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Fibronectin and collagen I and III expression was significantly higher in the TGF-β group at 48 h compared with the normal or Taxol group (P < 0.05, n = 6). Treatment with paclitaxel resulted in a decrease in fibronectin and collagen I and III expression (P < 0.05, n = 6); B: Western blotting analysis showing Smad2/3 protein expression in vitro following treatment with paclitaxel in HSCs. Phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3 but not total Smad2 or Smad3 expression was significantly higher in the TGF-β group at 48 h compared with the normal or Taxol group (P < 0.05, n = 6). Treatment with paclitaxel resulted in a decrease in phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 (P < 0.05, n = 6). Densitometric analyses were performed from six independent experiments. Each bar represents the mean ± SD for six animals. aP < 0.05 vs TGF-β group; dP < 0.01 vs normal or Taxol group (n = 6).
-
Citation: Zhou J, Zhong DW, Wang QW, Miao XY, Xu XD. Paclitaxel ameliorates fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells
via inhibition of TGF-β/Smad activity. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(26): 3330-3334 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i26/3330.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i26.3330