Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2010; 16(22): 2743-2753
Published online Jun 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i22.2743
Published online Jun 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i22.2743
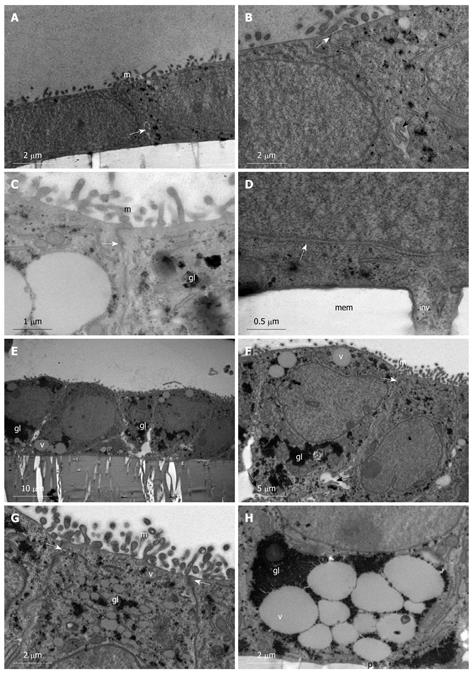
Figure 2 Spontaneous differentiation of Caco-2 into sub-population 2 of simple columnar monolayer of polarized epithelial cells.
A-D: Caco-2 cells grown on membrane filters examined on day 1 post-confluency. A: Simple cuboidal epithelium with regular microvilli (m) and intercellular junctions (white arrow); B: Intercellular junction with a tight junction (white arrow) evident along the apical part of the lateral plasma membrane. A small intercellular space (black arrow) is evident near the basolateral region of the plasma membrane; C: High power image of a tight junction (white arrow) between cells showing glycogen particles (gl) and microvilli (m); D: Basolateral plasma membrane showing intercellular junction (white arrow) and small invasive projection (inv) into the filter pore. Membrane (mem); E-H: Caco-2 cells grown on membrane filters examined on day 12 post-confluency. E: Simple columnar polarized epithelium is present with large glycogen stores (gl), mucin filled vacuoles (v), and intercellular spaces along the basal part of the lateral plasma membrane; F: Junction between two columnar cells (white arrow); regular microvilli (m) are present as well as large glycogen stores (gl) and mucin filled vacuoles (v). Intercellular space (black arrow); G: High power micrograph showing the apical domain of cells with regular microvilli (m), glycogen stores (gl), mucin vacuoles (v), and tight junction formation (white arrows); H: High power image of the basal domain of cells with large mucin filled vacuoles (v) enclosed by large glycogen stores (gl). No invasive processes are evident projecting into filter pores (p).
-
Citation: Biazik JM, Jahn KA, Su Y, Wu YN, Braet F. Unlocking the ultrastructure of colorectal cancer cells
in vitro using selective staining. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(22): 2743-2753 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i22/2743.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i22.2743