Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2010; 16(21): 2648-2656
Published online Jun 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i21.2648
Published online Jun 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i21.2648
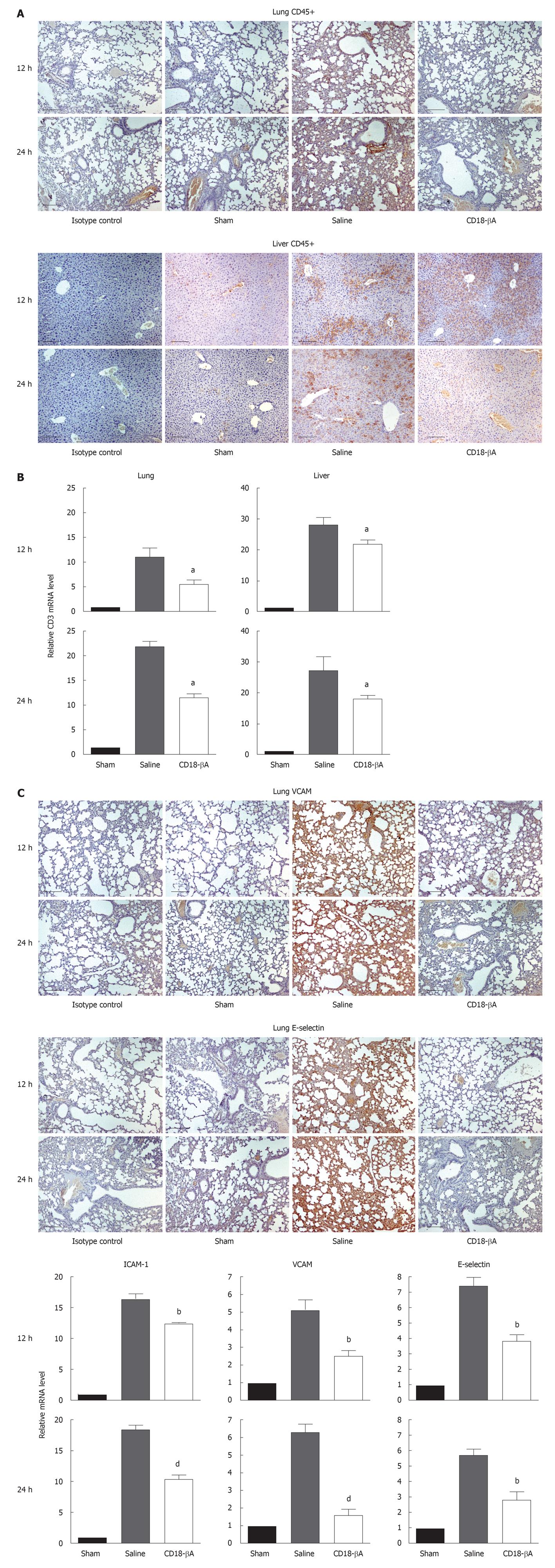
Figure 2 CD18-βA peptide inhibits CD45+ leukocyte infiltration into lung and liver in CLP-induced mice.
A: CD45+ leukocyte content in lung and liver after CLP was visualized by immunohistochemistry. Images are representative of n = 6 for each experimental group. Scale bar, 80 μmol/L; B: Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of CD3 mRNA level in lungs and liver, normalized to β-actin, at 12 and 24 h after CLP. Significant reductions in CD3 mRNA contents were observed in lungs and liver of septic mice that have been treated with CD18-βA peptide. aP < 0.05 vs saline group (one-way ANOVA); C: Pulmonary expression of adhesion molecules was studied using immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR. Lung sections were stained with VCAM and E-selectin antibody, and images are representative of n = 6 for each experimental group. Scale bars, 80 μm. Real-time PCR was employed to study mRNA expression of ICAM-1, VCAM, and E-selectin in lungs. Significant reductions in adhesion molecule mRNA contents were observed in lungs of septic mice that were treated with CD18-βA peptide. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 vs saline group (one-way ANOVA). For all real-time PCR study, n = 6 for each experimental group at 12 and 24 h. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
- Citation: Wong KF, Wo J, Ho D, Poon RT, Casasnovas JM, Luk JM. Prophylactic uses of integrin CD18-βA peptide in a murine polymicrobial peritonitis model. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(21): 2648-2656
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i21/2648.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i21.2648