Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2010; 16(19): 2378-2387
Published online May 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i19.2378
Published online May 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i19.2378
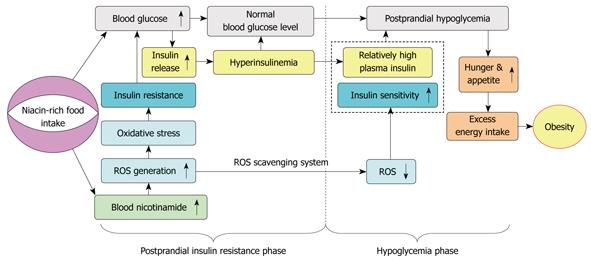
Figure 6 Proposed model of the role of niacin overload in obesity development.
Excess nicotinamide metabolism may induce a biphasic effect: postprandial hyperinsulinemia followed by postprandial hypoglycemia, in which reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and scavenging may play a central role.
- Citation: Li D, Sun WP, Zhou YM, Liu QG, Zhou SS, Luo N, Bian FN, Zhao ZG, Guo M. Chronic niacin overload may be involved in the increased prevalence of obesity in US children. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(19): 2378-2387
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i19/2378.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i19.2378