Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2010; 16(18): 2283-2290
Published online May 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i18.2283
Published online May 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i18.2283
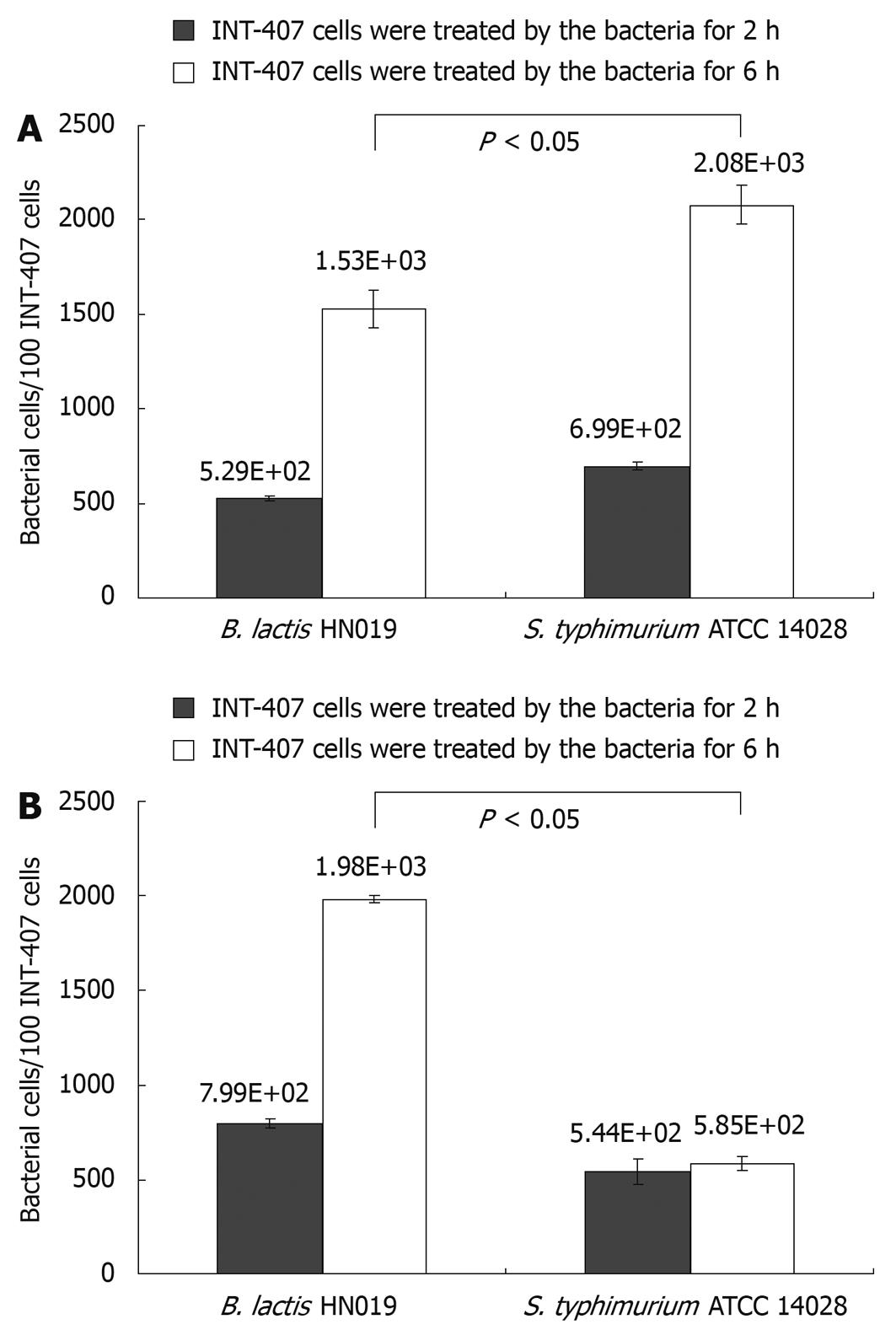
Figure 1 Adherence of Bifidobacterium lactis (B.
lactis) HN019 and Samonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) ATCC 14028 to INT-407 cells. A: Number of bacteria bound to 100 INT-407 cells obtained in assays contain each single strain; B: Number of bacteria bound to 100 INT-407 cells obtained in assays contain S. typhimurium ATCC 14028 plus B. lactis HN019. The error bars represent ± SD of the mean values.
-
Citation: Liu C, Zhang ZY, Dong K, Guo XK. Adhesion and immunomodulatory effects of
Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on intestinal epithelial cells INT-407. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(18): 2283-2290 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i18/2283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i18.2283