Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2010; 16(18): 2235-2243
Published online May 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i18.2235
Published online May 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i18.2235
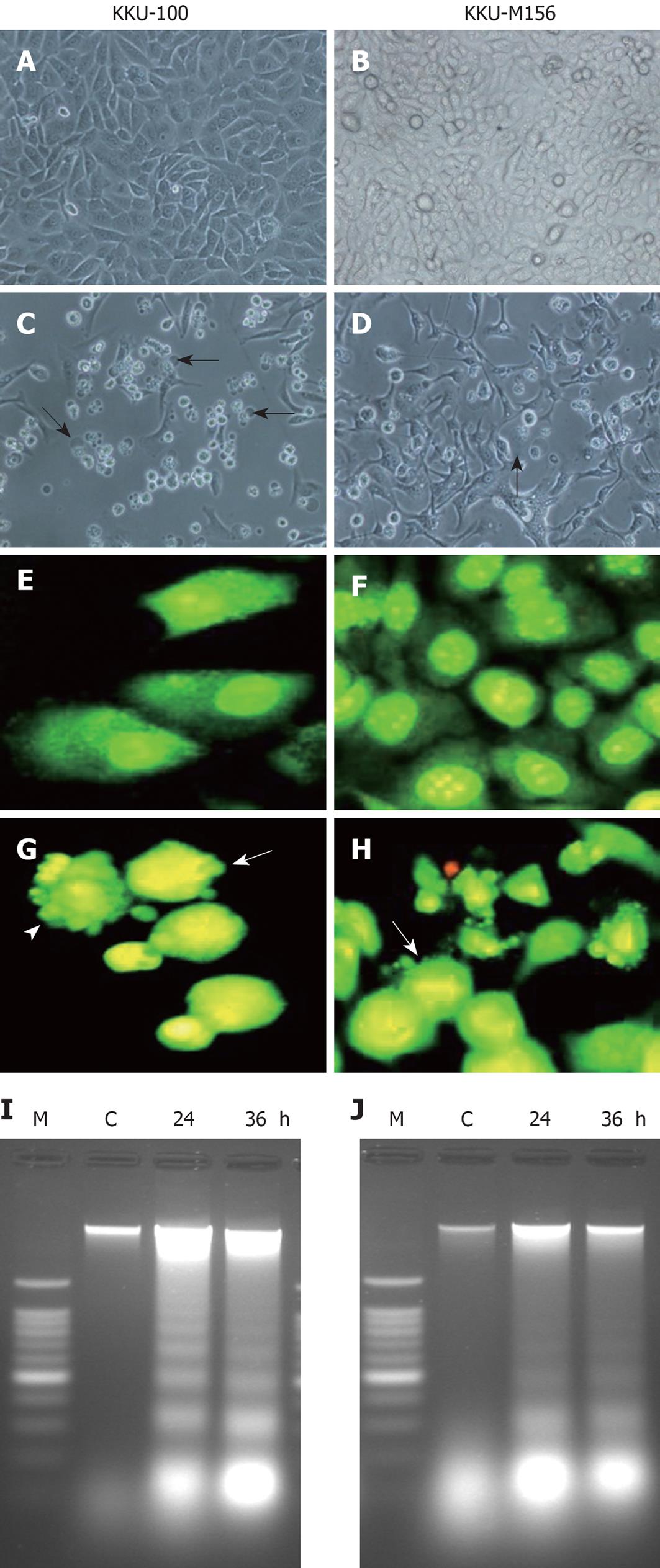
Figure 3 Induction of apoptosis in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell lines by four caged xanthones.
Photomicrographs (400 ×) of CCA cell lines KKU-100 (A, C) and KKU-M156 (B, D) treated with DMSO and gambogic acid for 48 h. A, B: Treated with DMSO; C, D: Treated with gambogic acid. Cells with membrane blebbing indicated by arrows; Fluorescence photomicrographs (400 ×) of CCA cell lines KKU-100 (E, G) and KKU-M156 (F, H) treated with DMSO and isomorellinol for 36 h followed by EB/AO staining. E, F: Treated with DMSO; G, H: Treated with isomorellinol. Nuclei of treated cells showing chromatin condensation (arrows) and nuclear fragmentation (arrow heads); DNA fragmentation of CCA cell lines treated with forbesione for the indicated times (24 h and 36 h). Genomic DNA was isolated and separated on 1.6% agarose gels containing 0.1 mg/mL ethidium bromide. I: KKU-100 cells; J: KKU-M156 cells. Lane C: DNA band of CCA cell lines treated with DMSO; Lane M: DNA markers. The figures show representative results of three independent experiments.
-
Citation: Hahnvajanawong C, Boonyanugomol W, Nasomyon T, Loilome W, Namwat N, Anantachoke N, Tassaneeyakul W, Sripa B, Namwat W, Reutrakul V. Apoptotic activity of caged xanthones from
Garcinia hanburyi in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(18): 2235-2243 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i18/2235.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i18.2235