Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2010; 16(17): 2094-2099
Published online May 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2094
Published online May 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2094
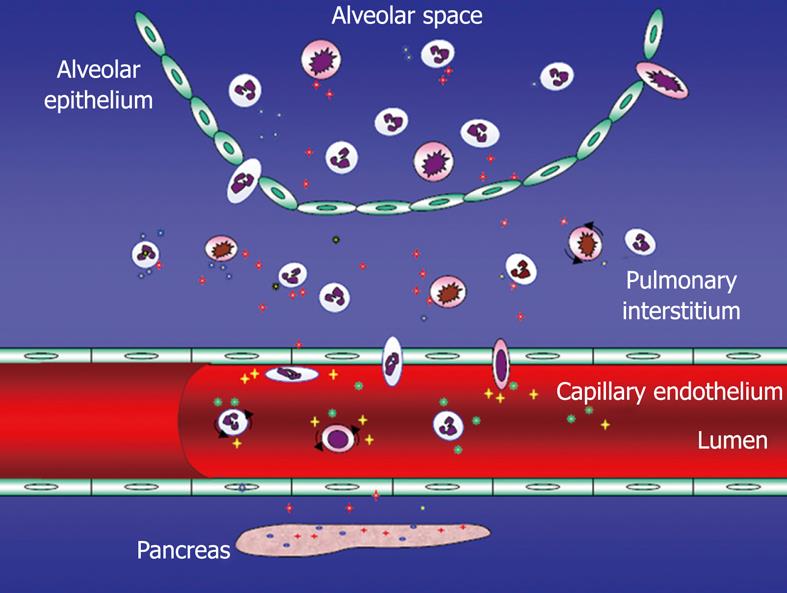
Figure 3 Acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury (ALI) - potential mechanisms including endothelial barrier dysfunction.
Several adhesion molecules [selectins, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) among others] involved in the extravasation of not at least polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). Tissue injury by not at least these PMNs.
- Citation: Zhou MT, Chen CS, Chen BC, Zhang QY, Andersson R. Acute lung injury and ARDS in acute pancreatitis: Mechanisms and potential intervention. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(17): 2094-2099
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i17/2094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2094