Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2010; 16(17): 2080-2093
Published online May 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2080
Published online May 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2080
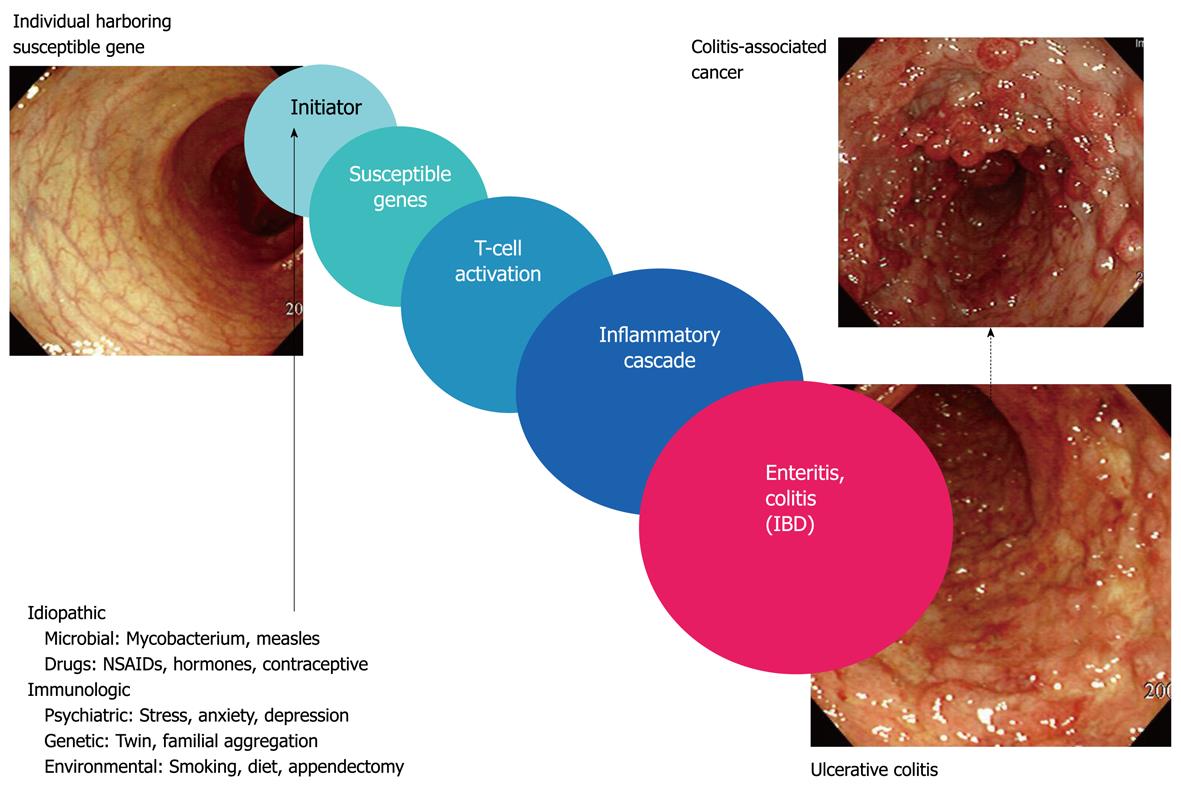
Figure 2 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colitis-associated cancer.
The cause of IBD is idiopathic because several etiologies have been suggested including microorganisms, drugs, psychiatric illness, genetic abnormality, and environmental factors. However, when individuals that harbor IBD susceptibility genes are exposed to the above-mentioned etiological factors, they experience T cell activation, after which perpetual inflammatory cascades lead to enteritis or colitis. Repeated bouts of chronic colitis alone provoke colitis-associated cancer, which emphasizes the cross-linking between inflammation and carcinogenesis. NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.
- Citation: Hong S, Lee HJ, Kim SJ, Hahm KB. Connection between inflammation and carcinogenesis in gastrointestinal tract: Focus on TGF-β signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(17): 2080-2093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i17/2080.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2080