Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2010; 16(16): 1953-1969
Published online Apr 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i16.1953
Published online Apr 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i16.1953
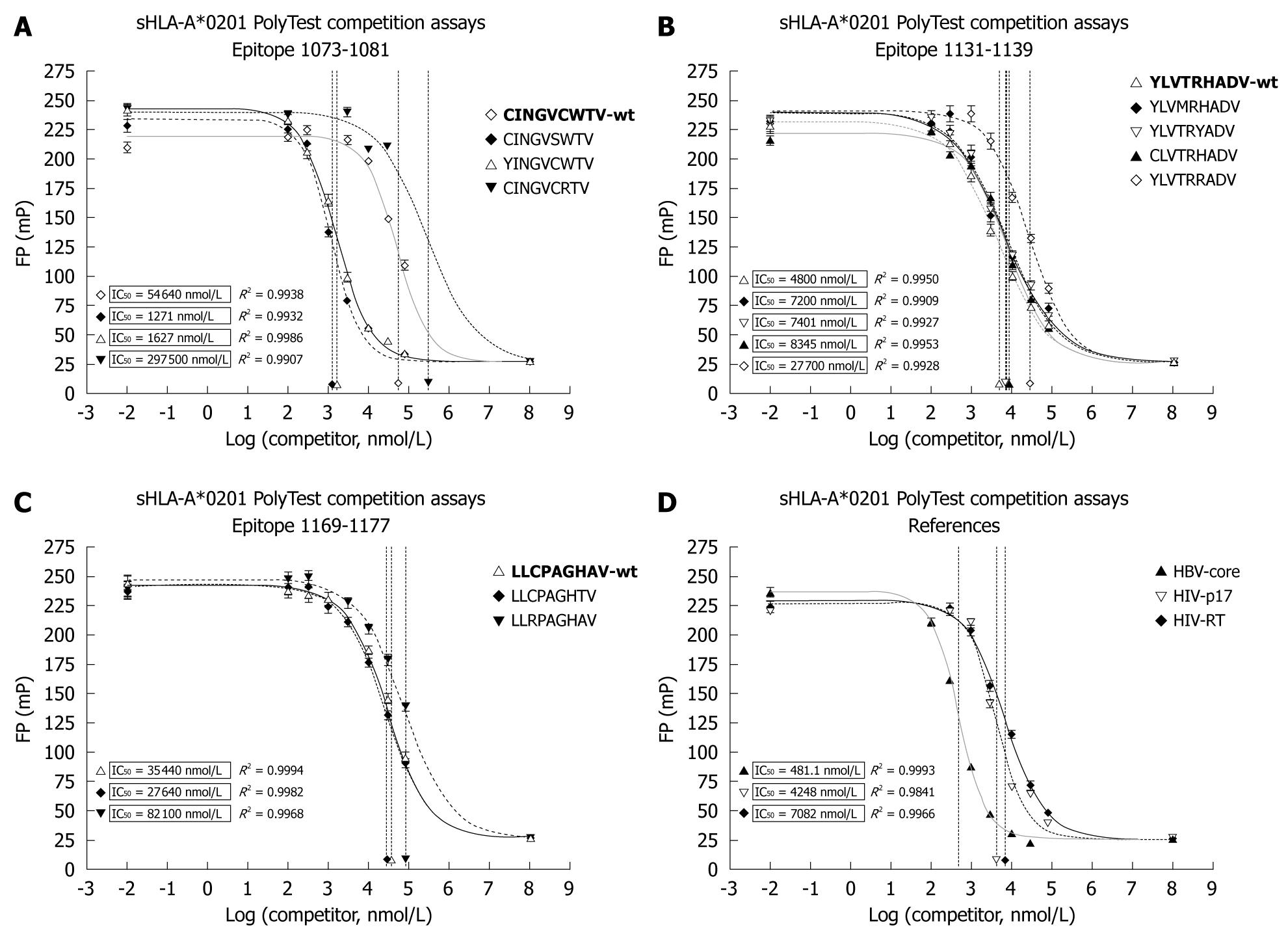
Figure 5 Soluble human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A*0201 competition assays determining the binding capacity (IC50) of natural HCV epitope variants.
The affinity of three wild type HCV peptide epitopes (bold) wt1073 (A), wt1131 (B), wt1169 (C) derived from three locations within the NS3 region and their variants C1073Y, C1078S and W1079R (A), Y1131C, T1134M, H 1136Y and H1136R (B), C1171R and A1176T (C) was determined. Control peptides HBV-Core, HIV-p17 and HIV-reverse transcriptase (RT) were included to provide reference values to other viral systems. Their affinities are presented in graph (D). For each experiment, 8 serial dilutions (100 nmol/L-80 μmol/L) of the unlabeled viral peptide were used to compete against a FITC-labeled tracer peptide. After reaching equilibrium, IC50 values for all peptides were determined by fitting the data to a dose-response model using the software Prism. R2 values indicate the goodness of fit.
- Citation: Wang S, Buchli R, Schiller J, Gao J, VanGundy RS, Hildebrand WH, Eckels DD. Natural epitope variants of the hepatitis C virus impair cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(16): 1953-1969
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i16/1953.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i16.1953