Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2010; 16(15): 1811-1819
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1811
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1811
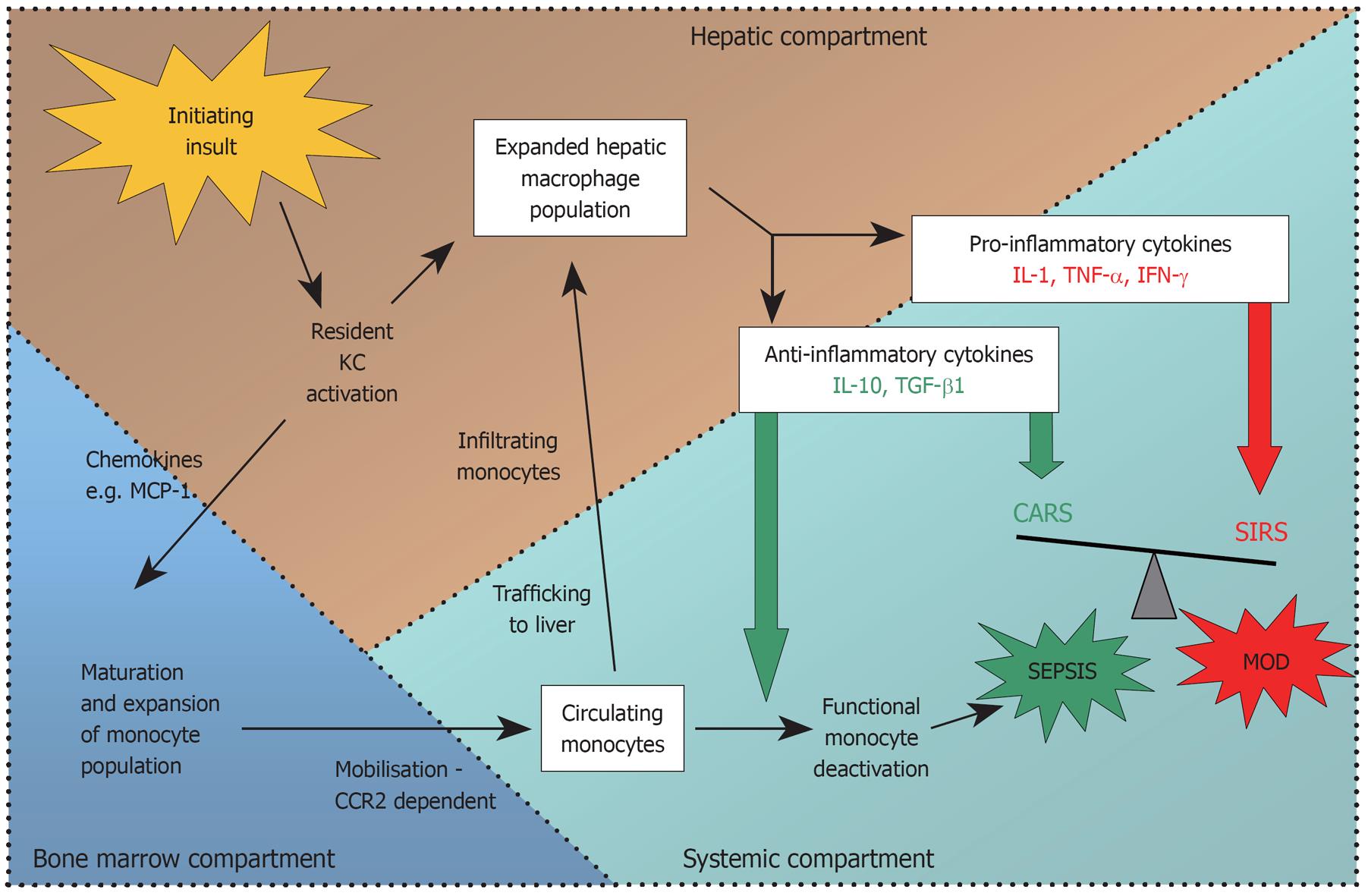
Figure 3 Summary of pathways.
The initiating hepatic insult causes early release of chemokines, which promote the maturation of a population of bone marrow monocytes. These activated monocytes enter the circulation and some will traffic to the liver and differentiate into macrophages, accounting for the marked expansion in hepatic macrophage numbers seen after acute liver injury. Pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines are released simultaneously, early in the course of ALF. High levels of both pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines can be measured in the systemic circulation and drive the systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) and compensatory anti-inflammatory response (CARS) respectively. Imbalance in these two opposing forces in favour of an anti-inflammatory milieu can lead to functional monocyte deactivation, recurrent sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction (MOD). MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; CCR2: Chemokine receptor 2.
- Citation: Possamai LA, Antoniades CG, Anstee QM, Quaglia A, Vergani D, Thursz M, Wendon J. Role of monocytes and macrophages in experimental and human acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(15): 1811-1819
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i15/1811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1811