Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2010; 16(14): 1759-1764
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1759
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1759
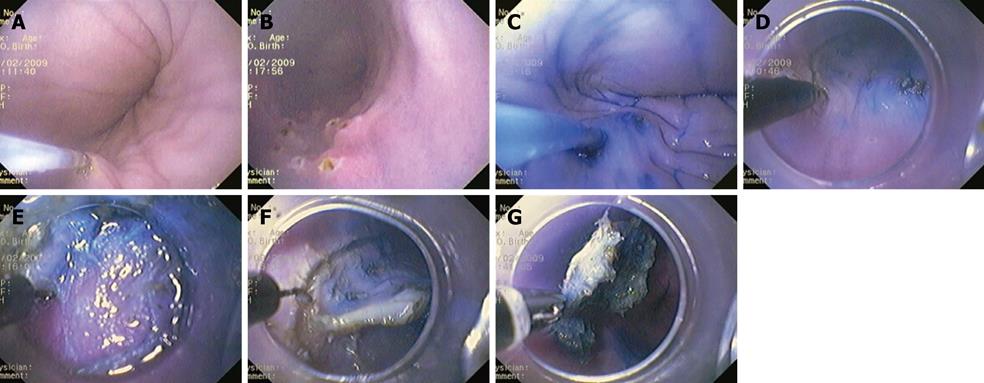
Figure 1 Procedure.
A, B: Artificial lesion marked with coagulation points; C: Injection of normal saline with epinephrine and indigo carmine; D: Knife cutting of a circumference around the lesion; E: Transparent softcap provides lesion counter-traction; F: Soft cap attached to the tip of the endoscope during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD); G: Grasping forceps during retrieval of ESD specimens.
- Citation: Tanimoto MA, Torres-Villalobos G, Fujita R, Santillan-Doherty P, Albores-Saavedra J, Gutierrez G, Martin-del-Campo LA, Bravo-Reyna C, Villanueva O, Villalobos JJ, Uribe M, Valdovinos MA. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in dogs in a World Gastroenterology Organisation training center. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(14): 1759-1764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i14/1759.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1759