Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2010; 16(11): 1337-1343
Published online Mar 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1337
Published online Mar 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1337
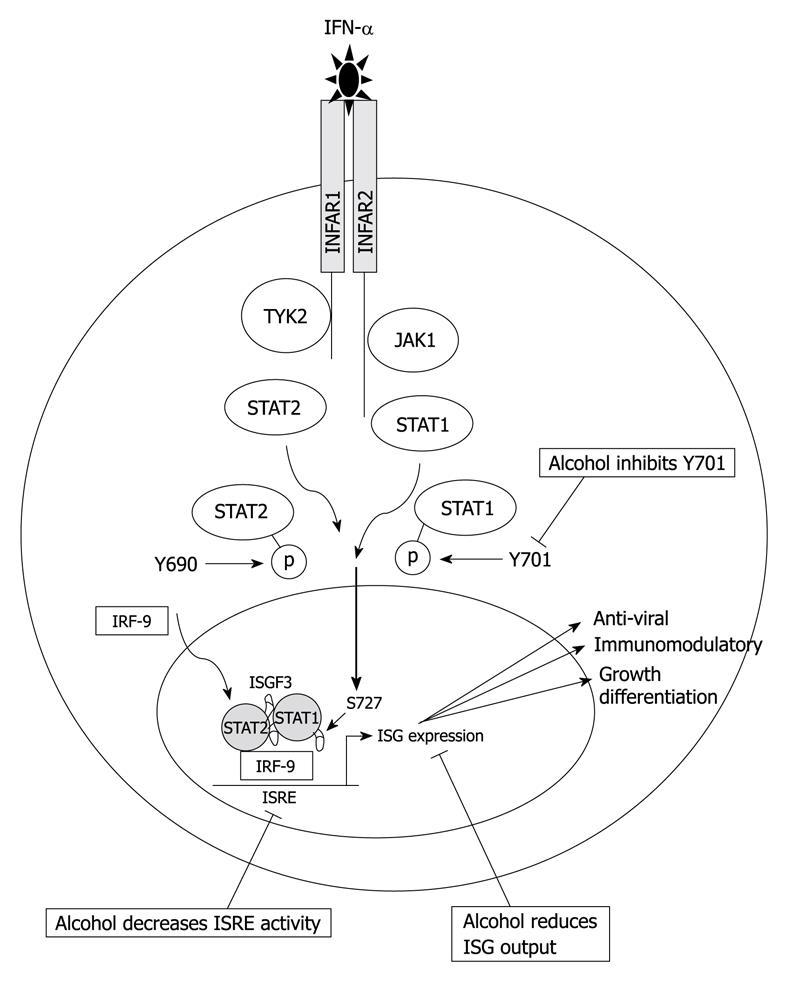
Figure 2 IFN-α signal transduction.
Binding of IFN-α to its cognate receptor on the cell surface results in activation of the Janus activated kinase (JAK)/STAT signaling pathway culminating in the production of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), many of which have anti-viral properties that act to limit HCV infection. Alcohol inhibits Y701, decreases interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) activity, and subsequently dampens the ISG response.
- Citation: McCartney EM, Beard MR. Impact of alcohol on hepatitis C virus replication and interferon signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(11): 1337-1343
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i11/1337.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1337