Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2010; 16(11): 1321-1329
Published online Mar 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1321
Published online Mar 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1321
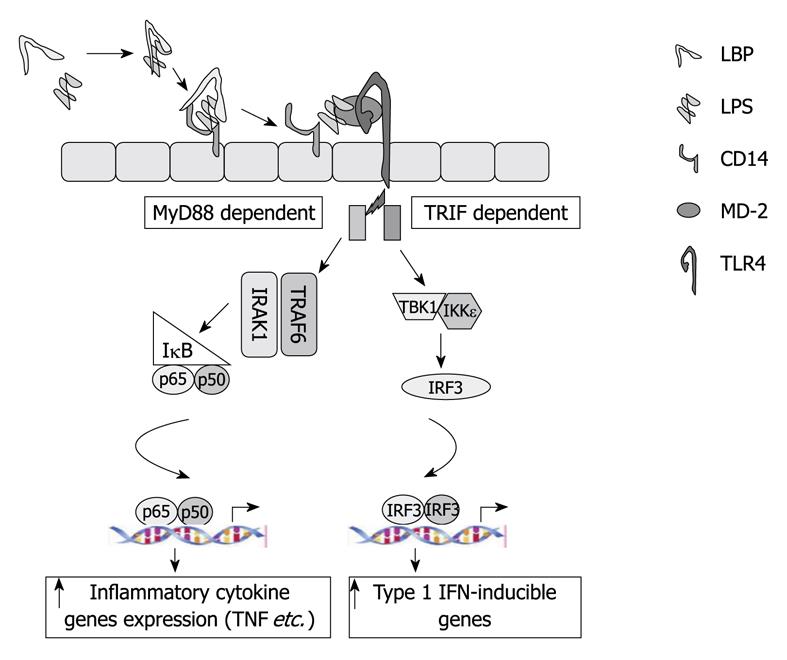
Figure 2 Role of the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-LPS signaling cascade in alcohol induced liver injury.
LPS binds to LPS binding protein (LBP), transfers to cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) and then to the TLR4 myeloid differentiation factor-2 (MD-2) complex. This signal is passed either through MyD88-dependent or TRIF-dependent intracellular pathways, which activate various transcription factors and induce various pro-inflammatory cytokine and Type I interferon genes.
- Citation: Szabo G, Bala S. Alcoholic liver disease and the gut-liver axis. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(11): 1321-1329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i11/1321.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1321