Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2010; 16(10): 1201-1208
Published online Mar 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i10.1201
Published online Mar 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i10.1201
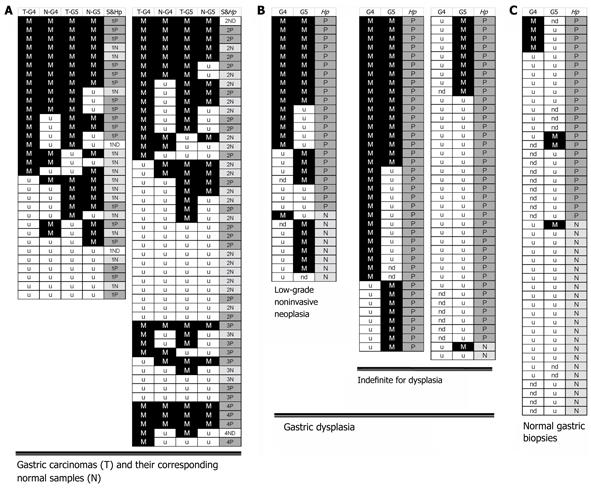
Figure 2 Summary of MSP results of GATA-4 and GATA-5 methylation in SGCs (A), gastric dysplasia (B), and normal gastric mucosa samples (C).
Each row represents a single sample. G4: GATA-4; G5: GATA-5; M in black, detection of methylated alleles; u in white, detection of unmethylated alleles only; ND in white, methylation information not available. T: Sporadic gastric carcinomas (SGC) tissue; N: SGC-paired corresponding normal tissue; S: Clinical stage (1-4) of SGCs; Hp: H. pylori infection positive (P in gray) or negative (N in light gray), detected with the 23S rRNA-PCR for the normal and corresponding normal gastric mucosa samples and with the 13C-urea breath test for subjects with gastric dysplasia. The GATA-4 methylation positive rate in low-grade GIN from patients with H. pylori infection was significantly higher than that from patients without infection (15/21 vs 1/7, P = 0.023). The GATA-5 methylation positive rate in low-grade GIN was significantly higher than that in indefinite for dysplasia (20/29 vs 35/75, P = 0.042). The GATA-4 and GATA-5 methylation rates in normal gastric biopsies were significantly lower than those in gastric dysplasia and SGC and the adjacent normal tissues (P < 0.001).
-
Citation: Wen XZ, Akiyama Y, Pan KF, Liu ZJ, Lu ZM, Zhou J, Gu LK, Dong CX, Zhu BD, Ji JF, You WC, Deng DJ. Methylation of
GATA-4 andGATA-5 and development of sporadic gastric carcinomas. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(10): 1201-1208 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i10/1201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i10.1201