Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2009; 15(5): 561-569
Published online Feb 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.561
Published online Feb 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.561
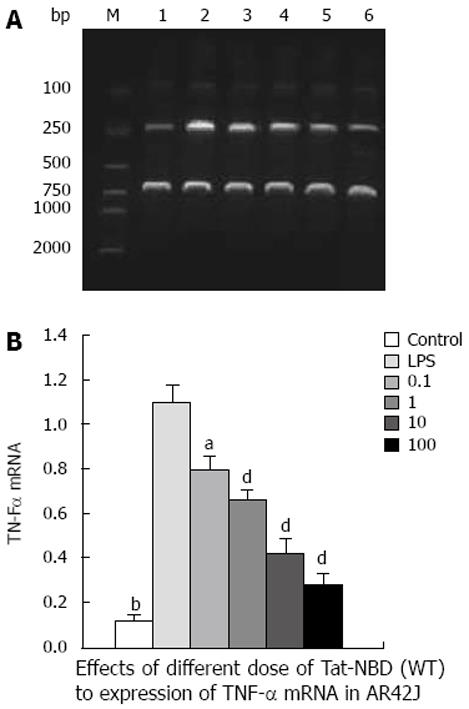
Figure 7 Effects of Tat-NBD (WT) in TNF-α mRNA expression of AR42J by RT-PCR.
A: Images of agarose gel electrophoresis; 1: Control; 2: LPS; 3: 0.1 mg/L Tat-NBD (WT); 4: 1 mg/L Tat-NBD (WT); 5: 10 mg/L Tat-NBD (WT); 6: 100 mg/L Tat-NBD (WT); M: Marker; B: TAT-NBD (WT) decreased TNF-α protein in a dose-dependent fashion over a range of 0.1 to 100 mg/L. Control: Cells were incubated with buffer control (n = 3); LPS: Cells were stimulated by LPS for 2 h (n = 3). 0.1: Pretreatment with 0.1 mg/L of Tat-NBD (WT) (n = 3); 1: Pretreatment with 1 mg/L of Tat-NBD (WT) (n = 3); 10: Pretreatment with 10 mg/L of Tat-NBD (WT) (n = 3); 100: Pretreatment with 100 mg/L of Tat-NBD (WT) (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs LPS group. dP < 0.01 vs LPS group.
- Citation: Long YM, Chen K, Liu XJ, Xie WR, Wang H. Cell-permeable Tat-NBD peptide attenuates rat pancreatitis and acinus cell inflammation response. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(5): 561-569
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i5/561.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.561