Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2009; 15(43): 5418-5424
Published online Nov 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5418
Published online Nov 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5418
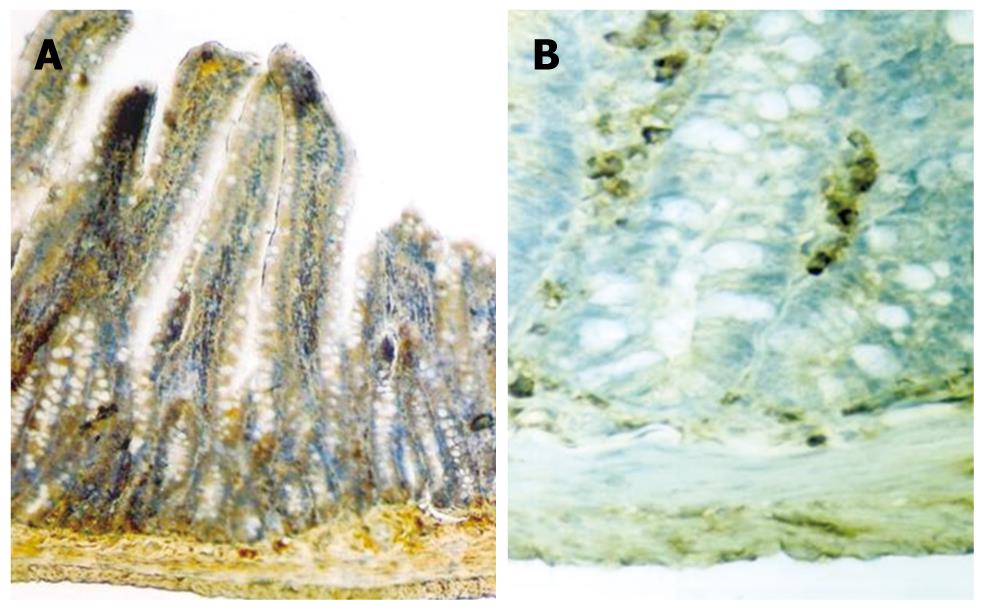
Figure 3 Like growth factor (IGF)-R immunoreactivity pattern in small intestines of the rats in the study group given growth hormone (A) and control group (B) by using the immuno-peroxidase technique.
While weak to moderate IGF-R immunostaining was observed in the epithelial cells of the small intestines in the control group, an increase in the immunostaining was seen in the study group. Note the strong immunoreactivity in the epithelial component and the moderately immunostained smooth muscle of the muscularis mucosa. Goblet cells display little or no immunoreactivity, in contrast to the dense immunoreaction in columnar cells of the study group. × 100 (Original magnifications).
- Citation: Ersoy B, Ozbilgin K, Kasirga E, Inan S, Coskun S, Tuglu I. Effect of growth hormone on small intestinal homeostasis relation to cellular mediators IGF-I and IGFBP-3. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(43): 5418-5424
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i43/5418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5418