Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2009; 15(42): 5260-5265
Published online Nov 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5260
Published online Nov 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5260
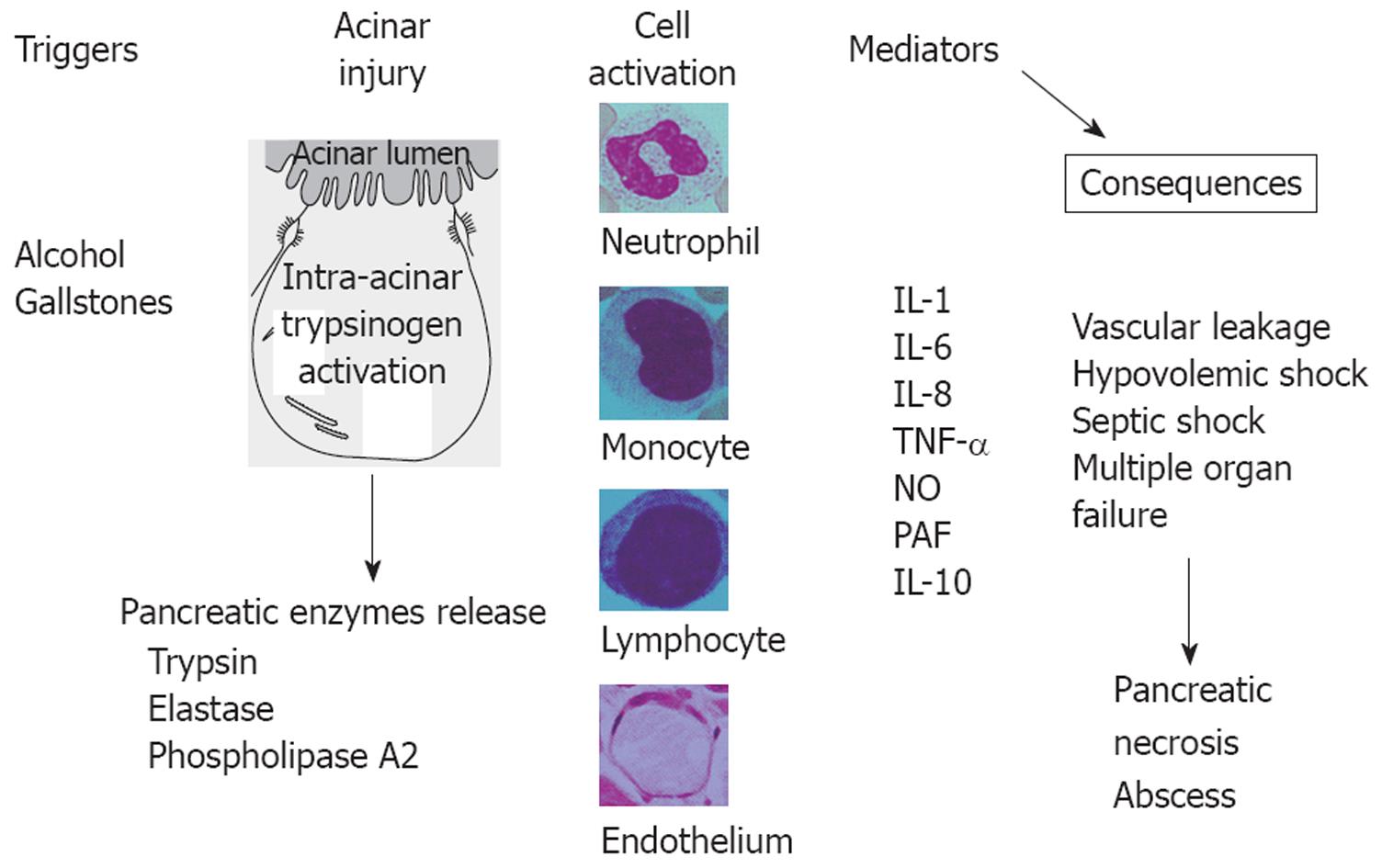
Figure 2 Mediators involved in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.
After the acinar cell injury occurs, inflammatory cells will synthesize and release proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines that induce systemic effects (vascular leakage, etc.). All these consequences will finally dictate the occurrence of pancreatic necrosis and abscess.
- Citation: Frossard JL, Lescuyer P, Pastor CM. Experimental evidence of obesity as a risk factor for severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(42): 5260-5265
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i42/5260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5260