Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2009; 15(41): 5149-5156
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5149
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5149
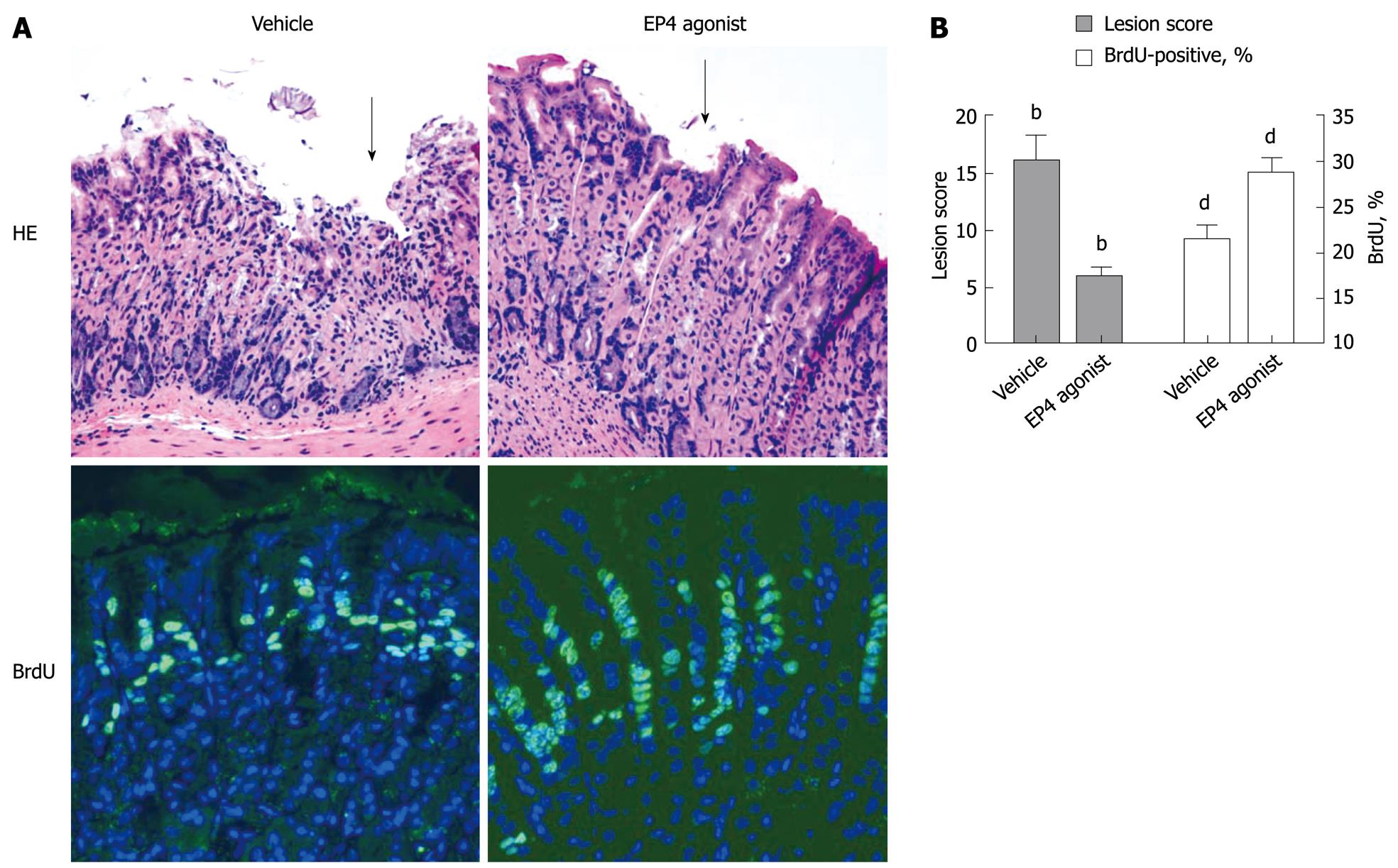
Figure 2 EP4 agonist effect on indomethacin-induced gastric lesion in mice.
EP4 agonist was orally administered 24 h and 30 min prior to indomethacin dosing at 20 mg/kg. The stomachs were assessed for mucus lesions 24 h after indomethacin dosing. A: HE and BrdU immunohistochemistry staining of stomachs (× 200). Superficial mucosal cells had sloughed off gastric mucus with infiltration of inflammatory cells in vehicle-treated group (arrow points to one lesion site). The mucus of EP4 agonist-treated stomachs was almost normal, except for a sparse focal defect of superficial mucous cells without inflammatory cells (arrow points to one lesion site). BrdU labeling showed robust mucous epithelial regeneration and migration in EP4 agonist-treated rats compared with that of vehicle treatment; B: Quantification of gross lesion under dissection microscopy (× 16) and percentage of BrdU-positive cells among mucus cells. Shown are lesion scores, bP < 0.0001, n = 10; and BrdU percentage, dP < 0.01, n = 10, respectively.
- Citation: Jiang GL, Im WB, Donde Y, Wheeler LA. EP4 agonist alleviates indomethacin-induced gastric lesions and promotes chronic gastric ulcer healing. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(41): 5149-5156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i41/5149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5149