Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2009; 15(41): 5129-5140
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5129
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5129
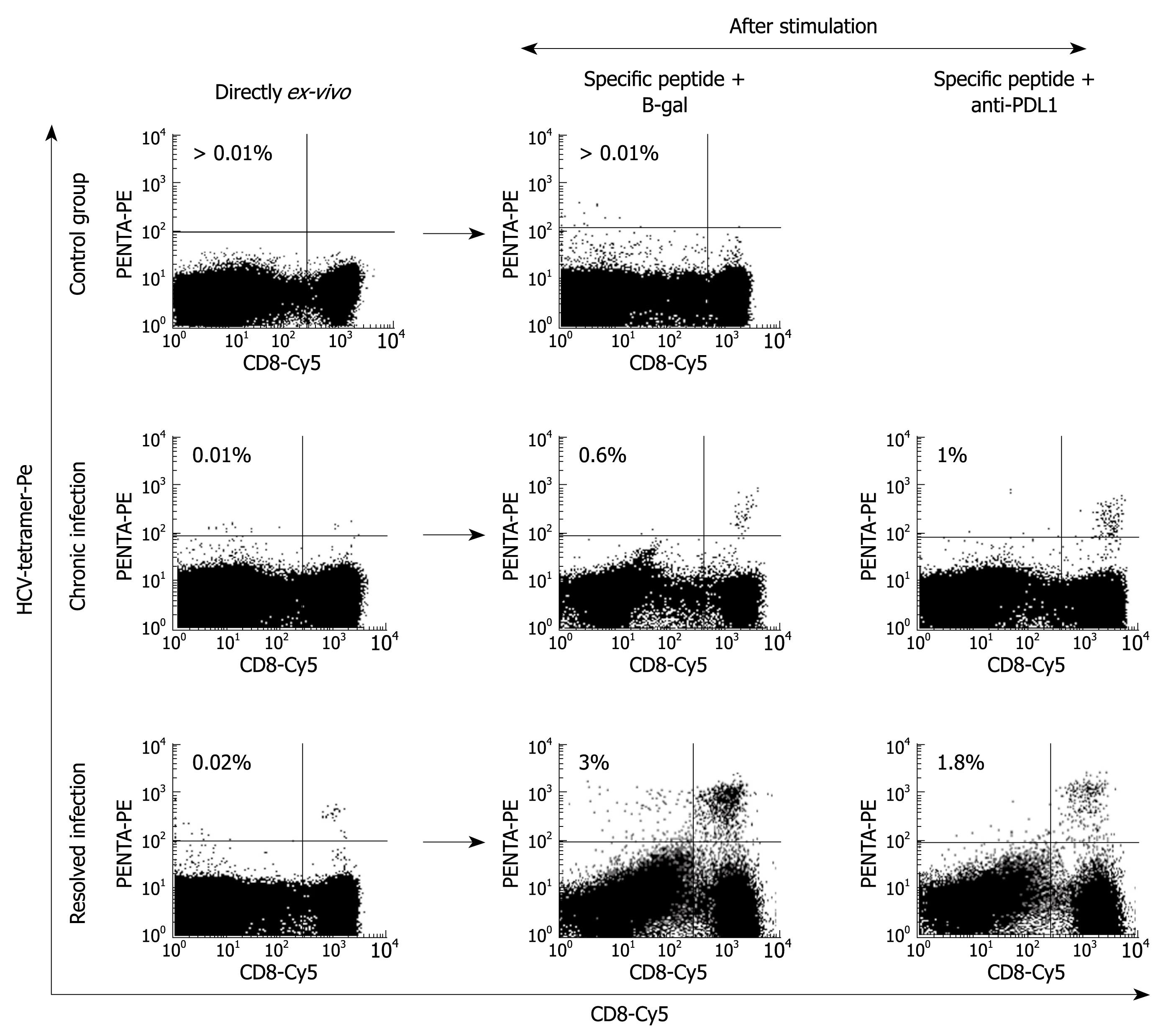
Figure 5 Proliferation restoration after PD-1 blockade.
FACS® dot-plots of peripheral blood T cells from two representative patients, one with persistent HCV infection and the other with resolved HCV infection, and a control case, after specific stimulation in the presence or absence of anti-PD-L1 mAb. T cells were stimulated for 10 d with the HCV–specific peptide plus IL-2. After stimulation, T cells were stained with CD8-Cy mAbs and HCV-tetramers-PE. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blockade by anti-PD-L1 antibodies increases the HCV-specific cell proliferation in the chronic patient that had a high level of PD-1 expression.
- Citation: Larrubia JR, Benito-Martínez S, Miquel J, Calvino M, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Parra-Cid T. Costimulatory molecule programmed death-1 in the cytotoxic response during chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(41): 5129-5140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i41/5129.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5129