Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2009; 15(41): 5129-5140
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5129
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5129
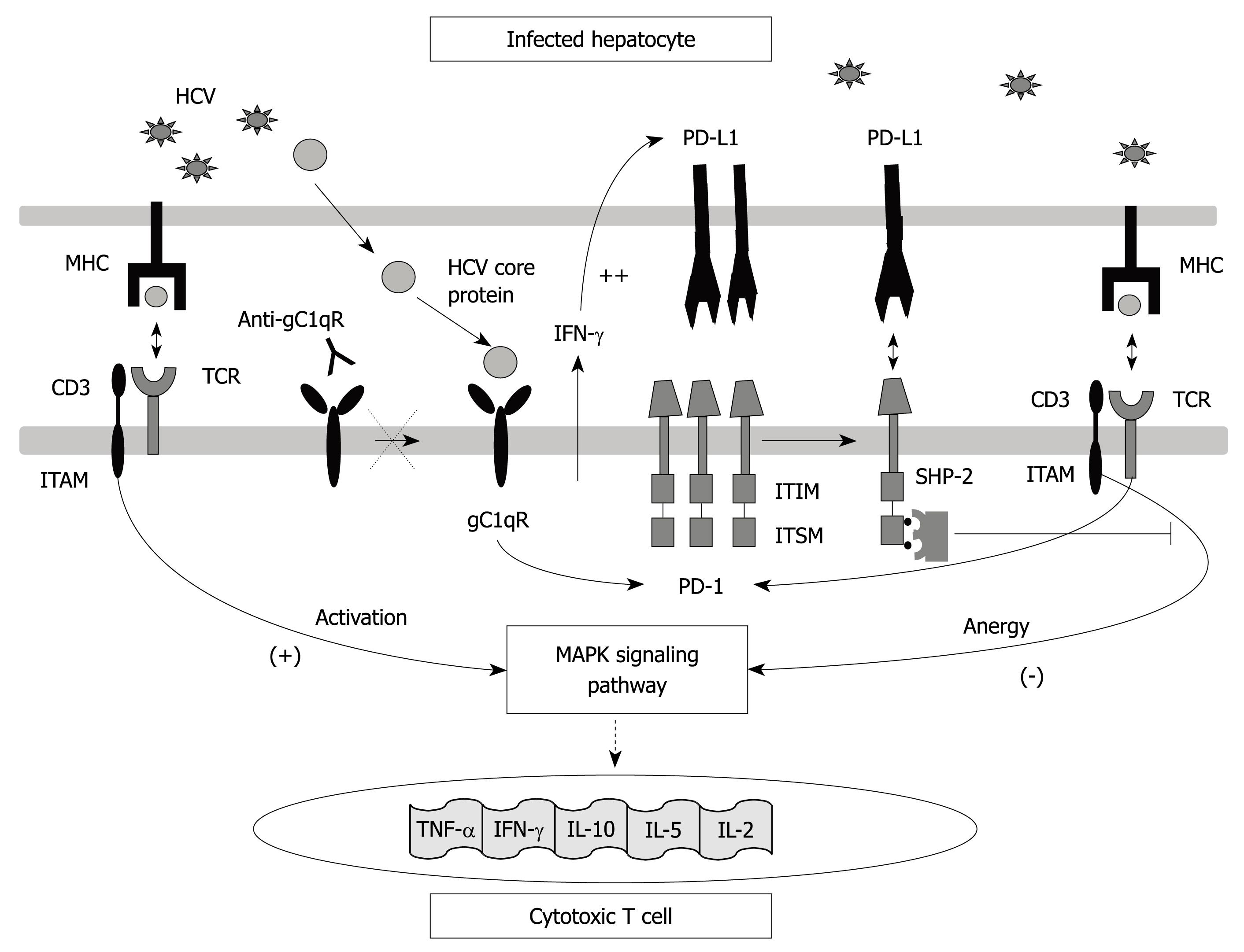
Figure 1 Programmed death-1 (PD-1) structure and interactions.
Interaction between the PD-1 molecule expressed on T cells and its ligand PD-L1 expressed on antigen-presenting cells leads to immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) motif phosphorylation in its cytoplasmic tyrosines which are recognized by src homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 (SHP-2). All of these interactions cause T cell anergy due to T cell receptor (TCR)-dependent MAP Kinase-pathway signalling inhibition which avoids interleukin (IL)-2 gene transduction. PD-1 expression is induced by TCR activation but could also be favoured by HCV-core protein through interaction with gC1qR. PD-L1 is up-regulated on antigen presenting cells by the effect of γ-interferon produced during HCV infection by activated lymphocytes.
- Citation: Larrubia JR, Benito-Martínez S, Miquel J, Calvino M, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Parra-Cid T. Costimulatory molecule programmed death-1 in the cytotoxic response during chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(41): 5129-5140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i41/5129.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5129