Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2009; 15(39): 4865-4876
Published online Oct 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4865
Published online Oct 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4865
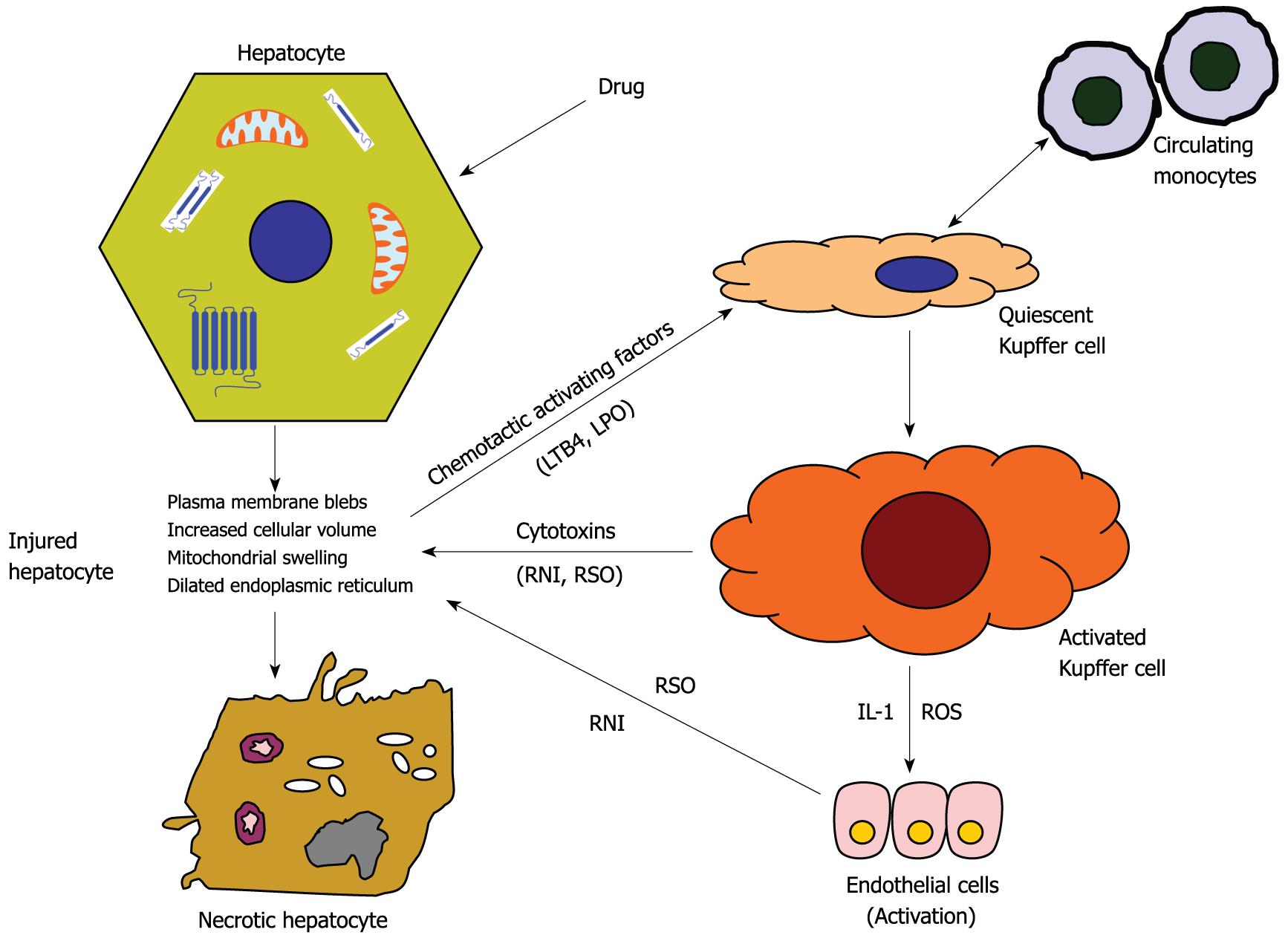
Figure 2 Schematic representation of toxic damage of hepatocyte in response to high dose of drug.
High drug amount is processed by hepatocytes with production of reactive metabolites which induce cell injury. Toxic products and chemotactic factors released by damaged hepatocytes stimulate the activation of Kupffer and endothelial cells with a subsequent delivery of reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen species. The intracellular damages result in necrotic death. LPO: Lipid peroxidation; LTB4: Leukotriene B4.
- Citation: Grattagliano I, Bonfrate L, Diogo CV, Wang HH, Wang DQ, Portincasa P. Biochemical mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: Certainties and doubts. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(39): 4865-4876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i39/4865.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4865