Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2009; 15(35): 4392-4401
Published online Sep 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4392
Published online Sep 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4392
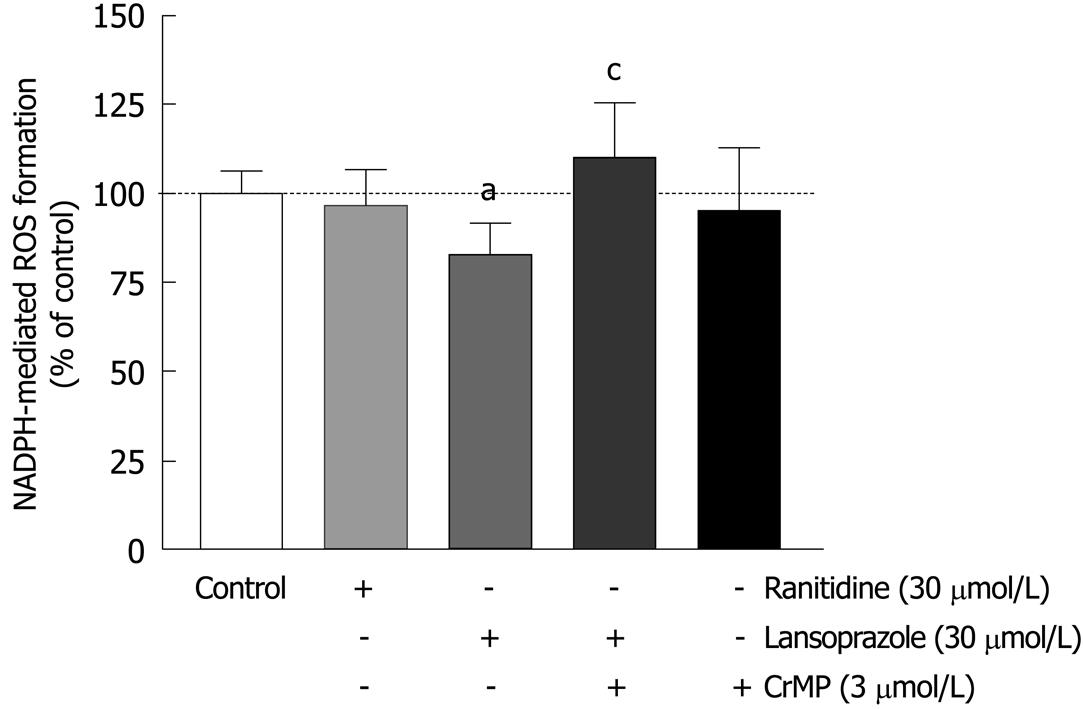
Figure 3 Lansoprazole, but not ranitidine, decreased NADPH-dependent ROS formation in macrophages.
This effect was reversed in the presence of CrMP. Measurements of lucigenin-enhanced chemiluminescence were performed. aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs lansoprazole alone. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three to six separate experiments.
- Citation: Schulz-Geske S, Erdmann K, Wong RJ, Stevenson DK, Schröder H, Grosser N. Molecular mechanism and functional consequences of lansoprazole-mediated heme oxygenase-1 induction. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(35): 4392-4401
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i35/4392.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4392