Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2009; 15(33): 4163-4169
Published online Sep 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4163
Published online Sep 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4163
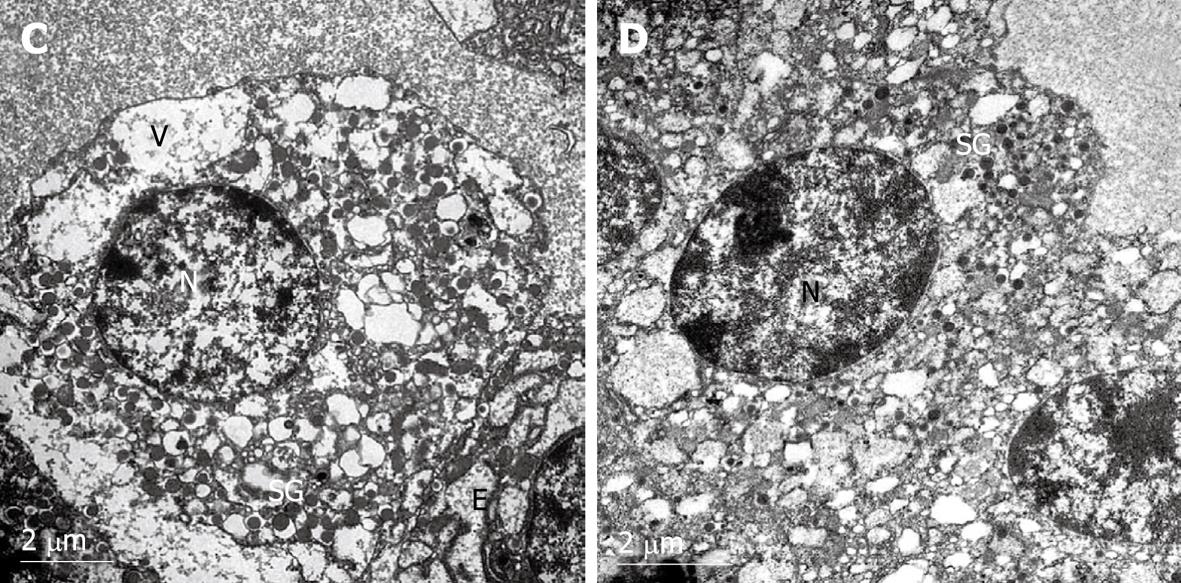
Figure 4 Electron micrographs of rat pancreatic islet β-cells after exposure to 30 ng/mL fentanyl for 48 h.
N: Nucleus; SG: Secretory granules; V: Vesicle; E: Endoplasmic reticulum. Chromatin margination and severe cytoplasmic vacuolization and degeneration were observed in the islets. Large and small vacuoles are present in the cytoplasm. The secretory granules and endoplasmic reticulum were much smaller than in the control group (A, × 10 000). In addition, endoplasmic reticulum and normal vesicles were almost never observed (B, × 12 000).
- Citation: Qian TL, Wang XH, Liu S, Ma L, Lu Y. Fentanyl inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin release from β-cells in rat pancreatic islets. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(33): 4163-4169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i33/4163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4163