Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2009; 15(27): 3382-3393
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3382
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3382
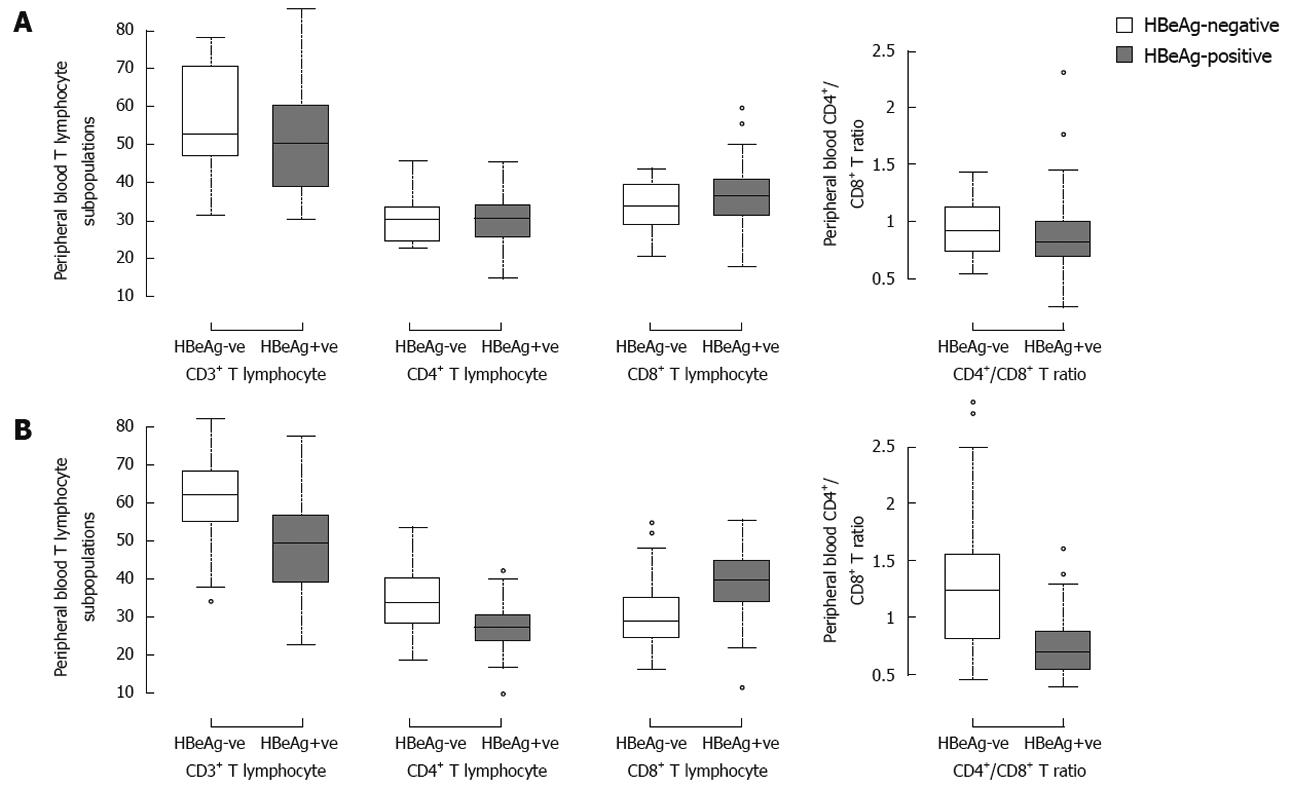
Figure 3 Mean percentages of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in peripheral blood of patients at the immune-tolerant stage (A) and immune active stage (B).
Patients were divided into two groups based upon the HBeAg status. The proportion of CD8+ T-cells was significantly higher in HBeAg positive patients than in HBeAg negative patients at the immune active stage (39.24 ± 8.05 vs 30.66 ± 8.01, P < 0.001). The percentage of CD4+ T-cells was significantly higher in HBeAg negative patients than in HBeAg positive patients at the immune active stage (33.60 ± 7.41 vs 27.39 ± 5.75, P < 0.001). Significant differences were found in CD3+ T-cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratio between HBeAg positive and negative patients (48.99 ± 11.06 vs 60.48 ± 11.22, 0.74 ± 0.25 vs 1.21 ± 0.50, P < 0.001). CD8+ T-cells were predominant compared with CD4+ T-cells in patients with a high HBeAg expression level, whereas CD4+ T-cells were predominant compared with CD8+ T-cells in patients with a low HBeAg expression level. In immune-tolerant-patients, no significant difference was observed in parameters of T-cell profile between HBeAg negative and positive patients (P > 0.05).
- Citation: You J, Zhuang L, Zhang YF, Chen HY, Sriplung H, Geater A, Chongsuvivatwong V, Piratvisuth T, McNeil E, Yu L, Tang BZ, Huang JH. Peripheral T-lymphocyte subpopulations in different clinical stages of chronic HBV infection correlate with HBV load. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(27): 3382-3393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i27/3382.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3382