Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2009; 15(27): 3382-3393
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3382
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3382
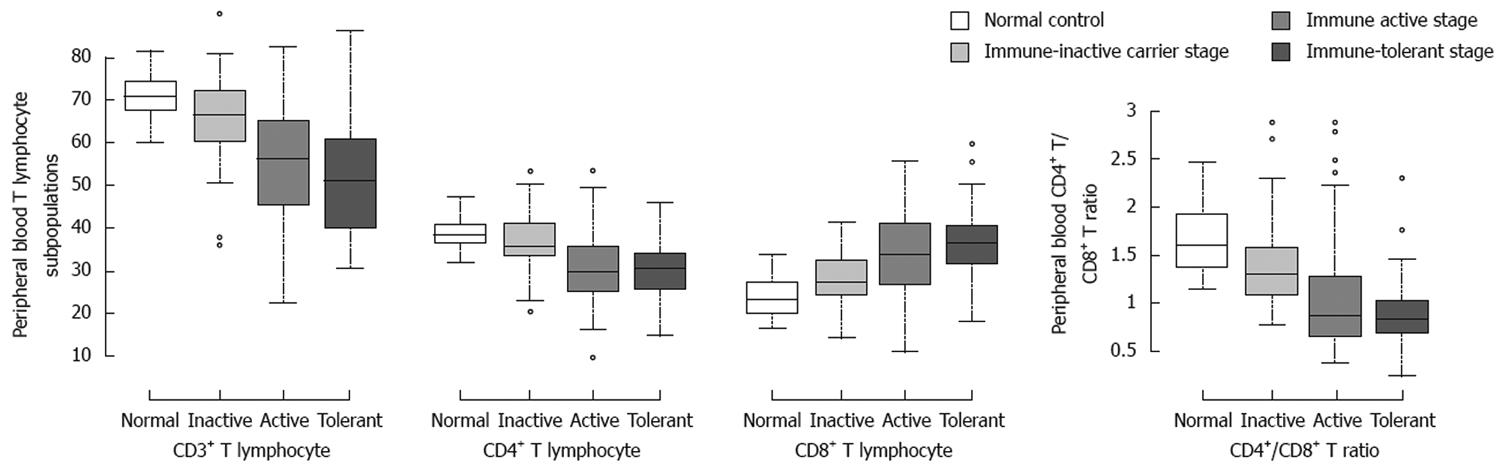
Figure 1 Peripheral blood T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients at different clinical stages of chronic HBV infection.
The mean percentages of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratio were shown in patients at the different stages and control. Top of the box represents the 75%, the bottom of the box represents the 25%, the solid line in the middle of the box represents the median. Whiskers above and below the box indicate the 90% and 10%, while filled circles represent outliers. A statistically significant difference in T cells but not in CD4+ cells was observed between chronic HBV infection patients and normal control (P < 0.01). In the peripheral blood of patients at the immune-tolerant and immune-active stages, CD8+ T-cells were the dominant lymphocytes compared to CD4+ T-cells, whereas in the peripheral blood of patients at the immune-inactive carrier stage and normal controls, CD4+ T-cells were the dominant lymphocytes compared to CD8+ T-cells.
- Citation: You J, Zhuang L, Zhang YF, Chen HY, Sriplung H, Geater A, Chongsuvivatwong V, Piratvisuth T, McNeil E, Yu L, Tang BZ, Huang JH. Peripheral T-lymphocyte subpopulations in different clinical stages of chronic HBV infection correlate with HBV load. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(27): 3382-3393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i27/3382.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3382