Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2009; 15(26): 3232-3239
Published online Jul 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3232
Published online Jul 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3232
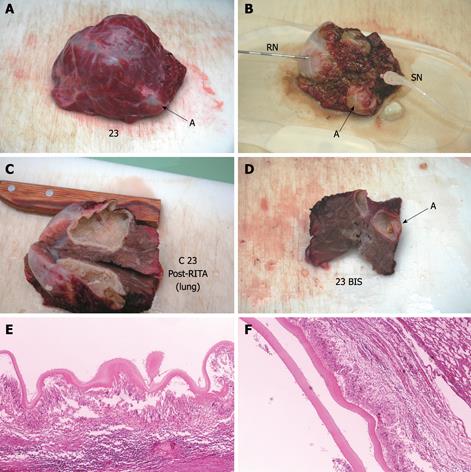
Figure 5 Echinococcus cyst of the lung before (A) and after (B-D) RTA.
External surface of the cyst (upper panel), findings after sectioning (middle panel), and histology (lower panel). After treatment (B) the cyst looks shrunken, rigid and dehydrated. Post-RTA section of the cyst (C) shows the endocyst is thick, papyraceous-like and attached to pericystium. Histology (HE stain, × 4) shows complete necrosis of the cyst wall (E). An adjacent cyst (indicated by arrow A in slides A, B, D) was necrotic and killed at histology (F) despite no direct treatment. RN: RITA needle; SN: Sentinel needle.
-
Citation: Lamonaca V, Virga A, Minervini MI, Di Stefano R, Provenzani A, Tagliareni P, Fleres G, Luca A, Vizzini G, Palazzo U, Gridelli B. Cystic echinococcosis of the liver and lung treated by radiofrequency thermal ablation: An
ex-vivo pilot experimental study in animal models. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(26): 3232-3239 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i26/3232.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3232