Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2009; 15(21): 2609-2616
Published online Jun 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2609
Published online Jun 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2609
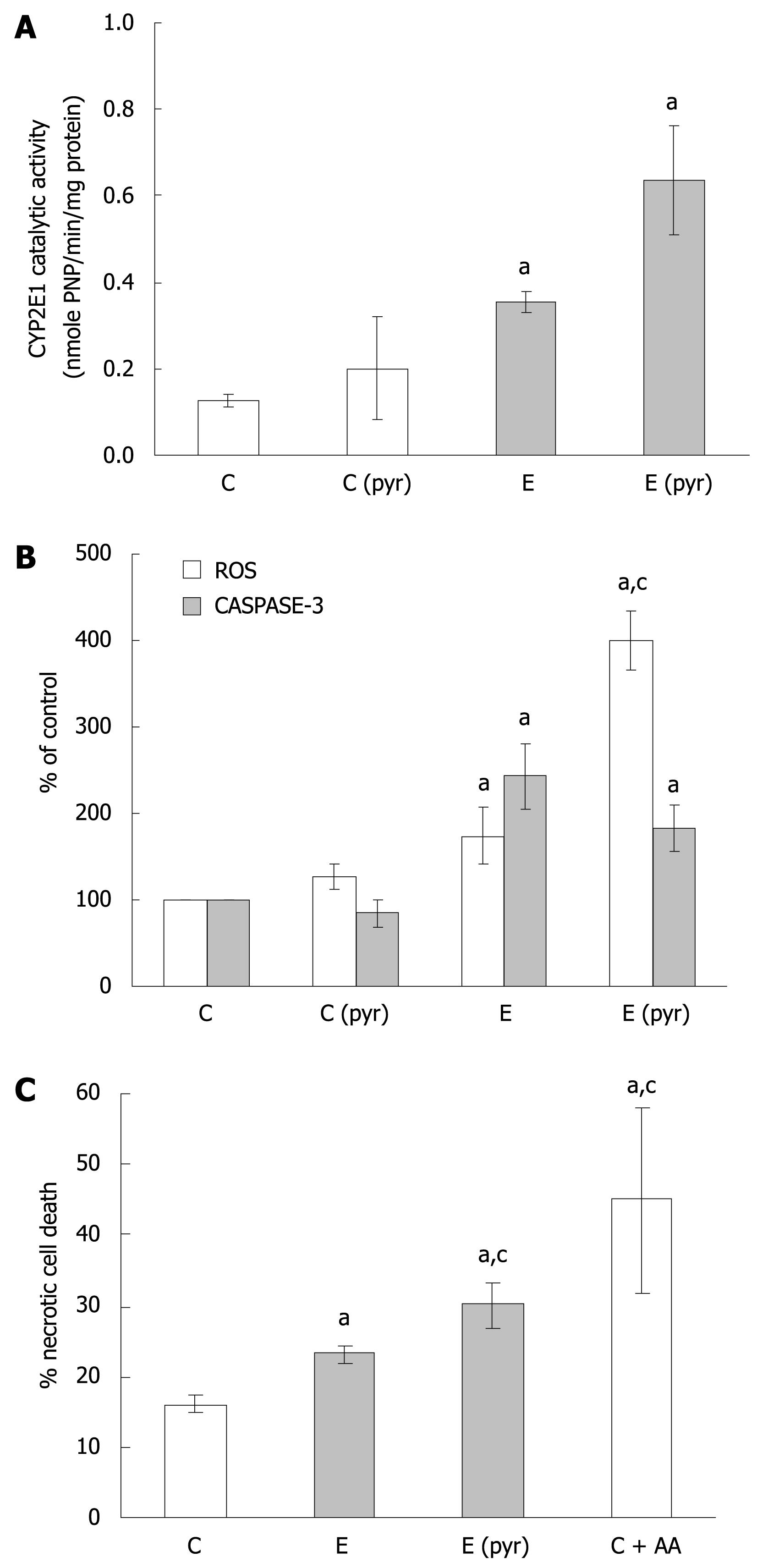
Figure 2 The relationship of CYP2E1 expression, oxidative stress, and WIF-B cell death following ethanol administration.
WIF-B cultures were treated without (C) or with pyrazole (Cpyr) for 4 d followed by ethanol treatment for 48 h [E and E (pyr)]. A: CYP2E1 activity in isolated microsomes analyzed using the r-nitophenol oxidation assay in four independent experiments; B: H2O2 production representative of ROS generation detected by dichlorofluorescein production, and the activation of caspase-3 as a measure of apoptosis from seven independent experiments; C: Necrotic cell death evaluated by flow cytometric analysis in three independent experiments using the LIVE/DEAD cell stain as described in “Material and Methods”. aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs ethanol alone-treated cells.
- Citation: McVicker BL, Tuma PL, Kharbanda KK, Lee SM, Tuma DJ. Relationship between oxidative stress and hepatic glutathione levels in ethanol-mediated apoptosis of polarized hepatic cells. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(21): 2609-2616
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i21/2609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2609