Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2009; 15(21): 2609-2616
Published online Jun 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2609
Published online Jun 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2609
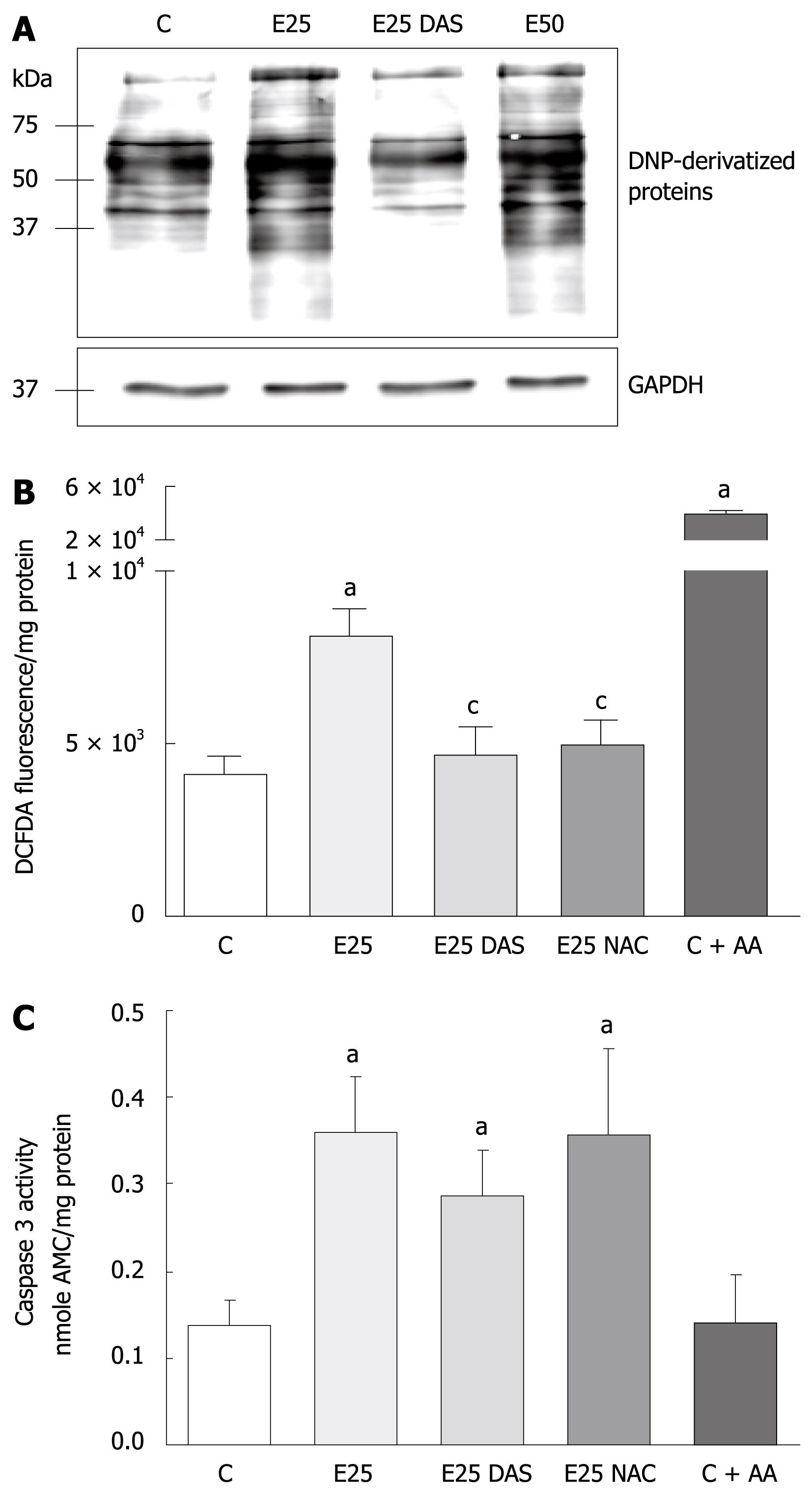
Figure 1 Ethanol-induced protein oxidation, oxidative stress, and caspase activation in WIF-B cells.
WIF-B cultures were cultured for 48 h in the absence or presence of ethanol, and DAS or NAC when indicated. As a positive control for H2O2 production, some cultures were treated with 2 &mgr;mol/L Antimycin A (C + AA) for 30 min prior to analysis. A: Protein oxidation analysis represented as DNP-specific proteins detected in WIF-B cell lysates using the OxyBlot protein oxidation analysis; B: H2O2 production was detected by dichlorofluorescein fluorescence quantification. Data from 5 independent experiments is represented as the amount of fluorescent (DCFDA) oxidized products detected in the treated cells per mg protein; C: The activation of the proapoptotic protease, caspase-3, was detected as described in “Material and Methods” for five independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs ethanol alone-treated cells.
- Citation: McVicker BL, Tuma PL, Kharbanda KK, Lee SM, Tuma DJ. Relationship between oxidative stress and hepatic glutathione levels in ethanol-mediated apoptosis of polarized hepatic cells. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(21): 2609-2616
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i21/2609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2609