Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2009; 15(2): 139-143
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.139
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.139
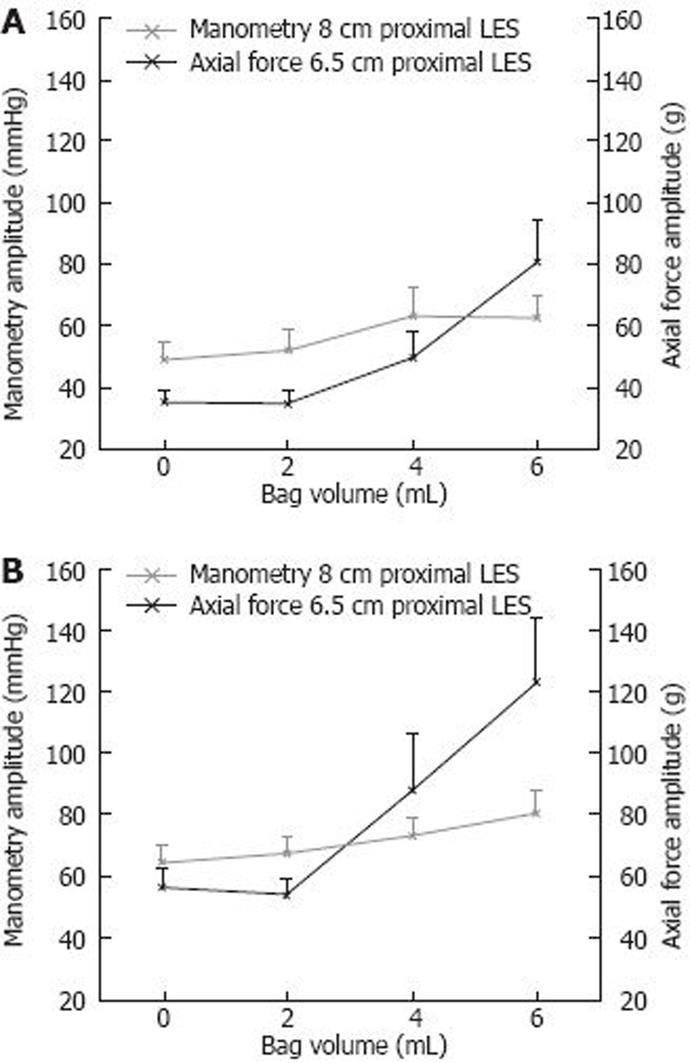
Figure 3 Swallow test with increased bag volume.
A: Dry swallow; B: Wet swallow. The pressure was recorded 8 cm proximal to the lower esophageal sphincter and the axial force was recorded 6.5 cm proximal to the lower esophageal sphincter. Both graphs show that the increased amplitude for axial force was greater when compared to manometry during both dry and wet swallows. Data are presented as mean ± SE from 10 volunteers.
- Citation: Gravesen FH, Funch-Jensen P, Gregersen H, Drewes AM. Axial force measurement for esophageal function testing. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(2): 139-143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i2/139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.139