Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2009; 15(11): 1346-1352
Published online Mar 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1346
Published online Mar 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1346
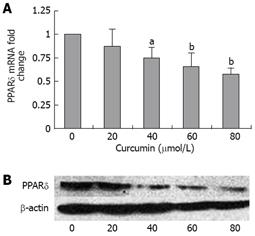
Figure 3 Curcumin inhibits the expression of PPARδ in HT-29 cells.
A: Real-time quantitative RT-PCR indicated that curcumin markedly reduced the level of PPARδ mRNA. Values are % reduction in PPARδ mRNA fold changes caused by curcumin compared with cells without curcumin treatment. Values are mean ± SD from three samples per group. GAPDH was used as an internal control; B: The effects of curcumin on the level of PPARδ protein were determined by Western blotting. β-actin was used as an internal marker. (aP < 0.05 vs control; bP < 0.01 vs control).
- Citation: Wang JB, Qi LL, Zheng SD, Wang HZ, Wu TX. Curcumin suppresses PPARδ expression and related genes in HT-29 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(11): 1346-1352
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i11/1346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1346