Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2009; 15(10): 1186-1193
Published online Mar 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1186
Published online Mar 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1186
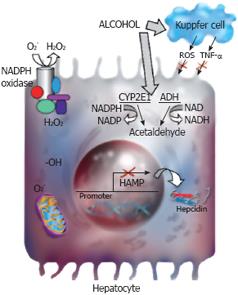
Figure 2 Hepcidin and alcohol.
Alcohol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) in the liver. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress leads to the suppression of hepcidin promoter activity and hepcidin transcription in the liver. The parenchymal, but not the non-parenchymal cells of the liver are involved in the regulation of hepcidin transcription by alcohol-induced oxidative stress. The activation of CYP2E1 or NADPH oxidase and changes in mitochondrial functions are involved in alcohol-induced oxidative stress in hepatocytes. The role of these pathways in the regulation of hepcidin transcription by alcohol requires further investigation.
- Citation: Harrison-Findik DD. Is the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin a risk factor for alcoholic liver disease? World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(10): 1186-1193
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i10/1186.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1186