Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2008; 14(9): 1346-1352
Published online Mar 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1346
Published online Mar 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1346
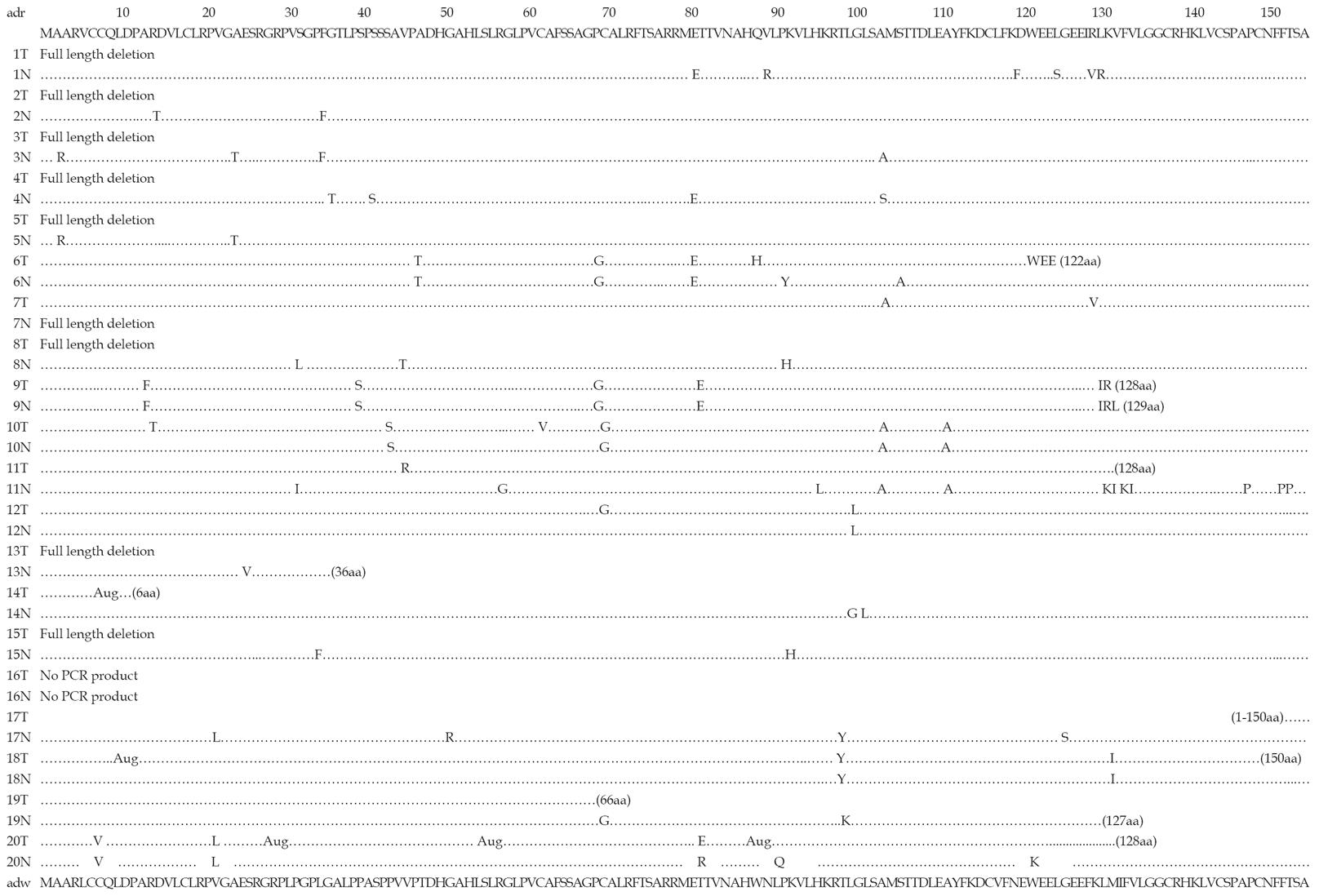
Figure 2 HBx sequencing in cancer and non-cancerous tissues from 20 HBV-associated HCC patients.
The amino acid sequences of HBV adr and adw subtypes are shown at the top or the bottom. Identical amino acid residues are represented by dots. The underlined amino acids were deduced from cellular flanking sequences. The frequencies of HBx point mutations were significantly lower in HCC than in the corresponding non-cancerous liver tissues (11/19 vs 18/19, P = 0.019). T: Tumor; N: Non-tumor. “…”: Represent the corresponding PCR amplificated base sequences.
- Citation: Liu XH, Lin J, Zhang SH, Zhang SM, Feitelson MA, Gao HJ, Zhu MH. COOH-terminal deletion of HBx gene is a frequent event in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(9): 1346-1352
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i9/1346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.1346