Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2008; 14(48): 7309-7320
Published online Dec 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7309
Published online Dec 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7309
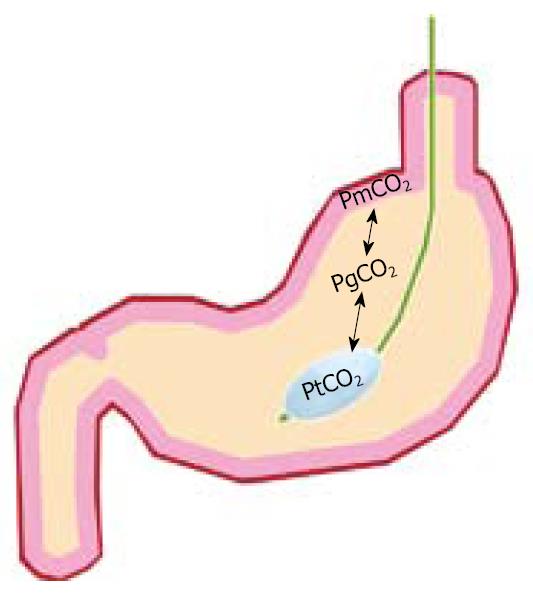
Figure 3 Tonometer balloon placed in the stomach nasogastrically.
CO2 diffuses rapidly over different membranes, therefore the tonometer PCO2 (PtCO2) will be in equilibrium with gastric luminal PCO2 (PgCO2) and mucosal PCO2 (PmCO2). The PCO2 can be measured from the catheter either from injected saline using blood gas analyzers or by connection to a semi-automated Tonocap device. The underlying physiological principle is that ischemia is always associated with PCO2 increase. Therefore, focal measurement of ischemia is possible for long periods via a minimally invasive technique.
- Citation: Kolkman JJ, Bargeman M, Huisman AB, Geelkerken RH. Diagnosis and management of splanchnic ischemia. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(48): 7309-7320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i48/7309.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.7309