Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2008; 14(47): 7149-7159
Published online Dec 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7149
Published online Dec 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7149
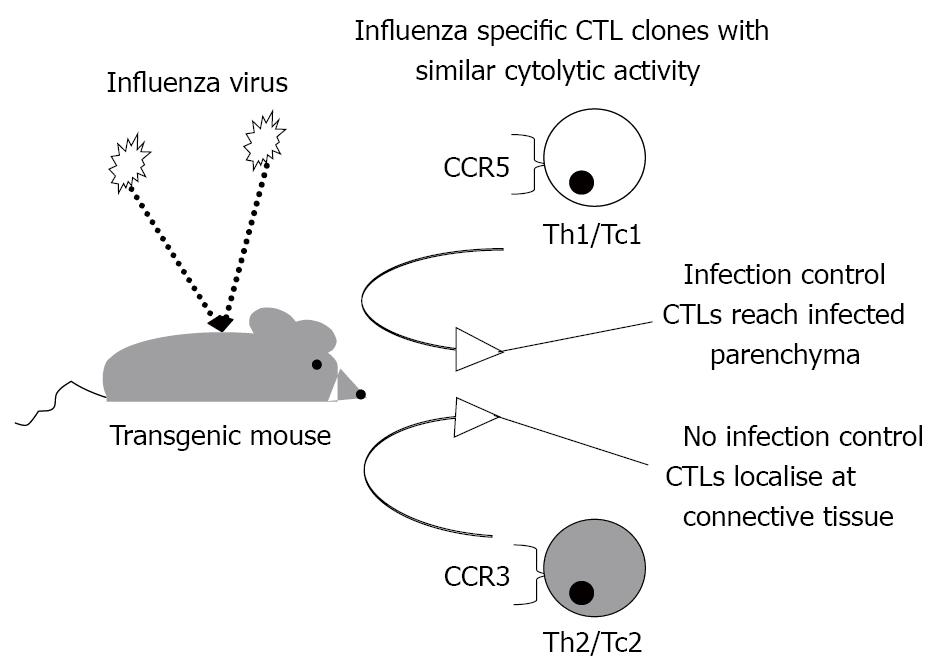
Figure 4 Adequate chemotaxis is necessary to control a viral infection.
Specific cytotoxic T cells with active in vitro effector functionality are not able to control a viral infection if they do not express the appropriate chemokine receptor to reach the infected parenchyma. In a murine model of influenza virus infection, specific CCR5-expressing T cells were able to clear the virus while administration of specific CCR3-expressing T cells induced mouse death. CTLs: cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
- Citation: Larrubia JR, Benito-Martínez S, Calvino M, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Parra-Cid T. Role of chemokines and their receptors in viral persistence and liver damage during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(47): 7149-7159
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i47/7149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.7149