Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2008; 14(44): 6786-6801
Published online Nov 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6786
Published online Nov 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6786
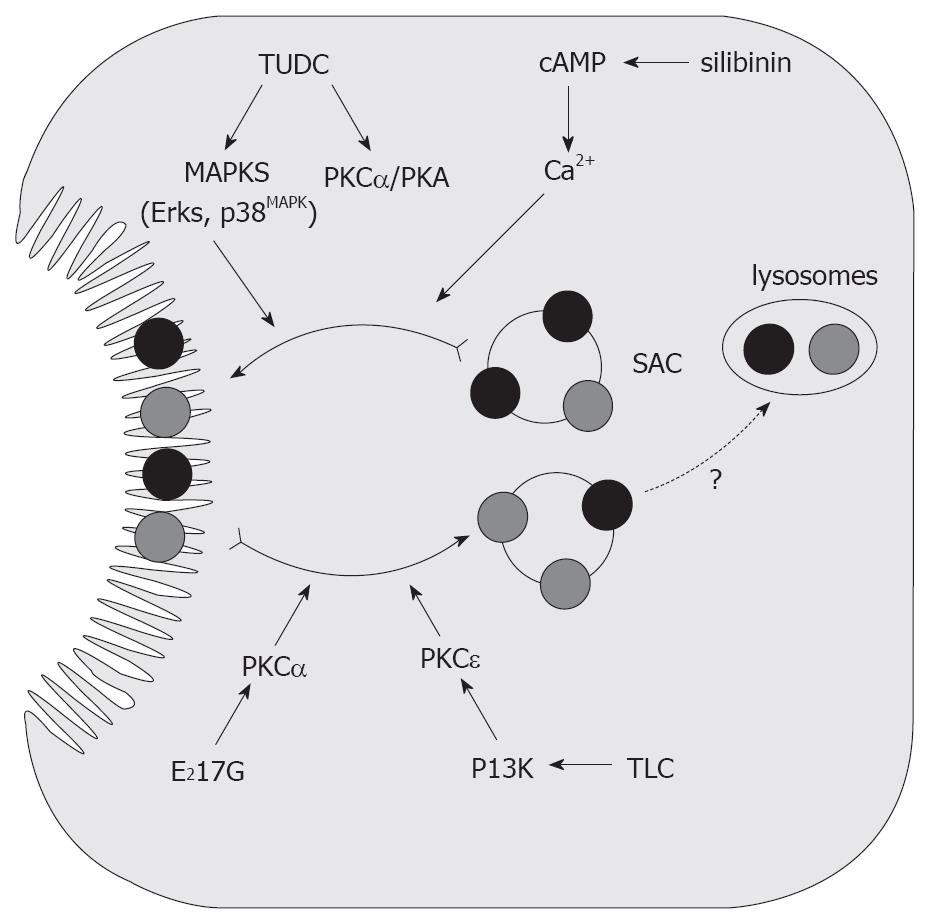
Figure 6 Endocytic internalization of canalicular transporters in E217G and in TLC-induced cholestasis.
Protection from these cholestatic agents by the anticholestatic agents cAMP and TUDC is also shown. E217G and TLC induce endocytic internalization of canalicular transporters into the subapical compartment (SAC); this may lead to delivery to the lysosomal compartment, followed by degradation. E217G-induced activation of PKCα and TLC-induced, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent activation of PKCε have been proposed to mediate this retrieval. Elevation of intracellular cAMP levels induced by administration of the permeant cAMP analogue DBcAMP, or by the phosphodiesterase inhibitor silibinin, prevents internalization, and accelerates re-insertion, via cytosolic Ca2+ elevations. On the other hand, TUDC prevents transporter endocytosis probably via co-stimulation of PKCα- and PKA-dependent pathways.
- Citation: Roma MG, Crocenzi FA, Mottino AD. Dynamic localization of hepatocellular transporters in health and disease. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(44): 6786-6801
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i44/6786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6786