Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2008; 14(43): 6601-6615
Published online Nov 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6601
Published online Nov 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6601
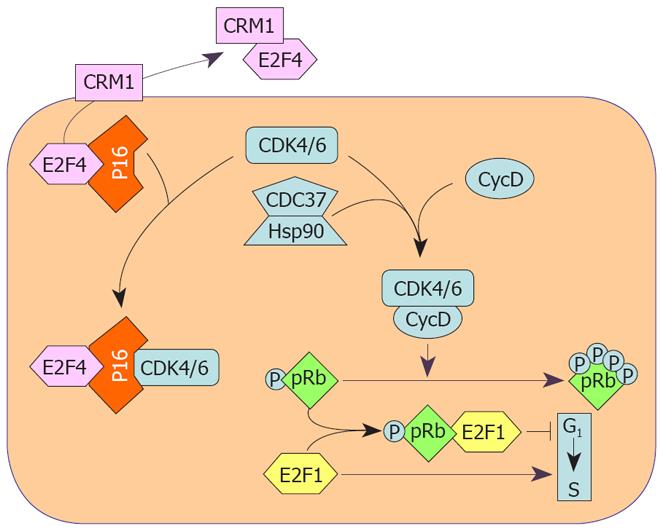
Figure 1 Cell cycle protection from inhibition by P16INK4A through the CDC37-HSP90 complex and CRM1 transporter protein.
P16INK4A forms complexes with CDK4 and CDK6 which, as a consequence, cannot by activated by Cyclin D1 and cannot phosphorylate pRb. The chaperons CDC37 and HSP90 form complexes with CDKs protecting them from inactivation by P16INK4A. CRM1 forms a complex with E2F4, a P16INK4A effector, transporting it outside of the nucleus, thus inactivating P16INK4A.
- Citation: Feo F, Frau M, Pascale RM. Interaction of major genes predisposing to hepatocellular carcinoma with genes encoding signal transduction pathways influences tumor phenotype and prognosis. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(43): 6601-6615
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i43/6601.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6601