Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2008; 14(42): 6473-6480
Published online Nov 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6473
Published online Nov 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6473
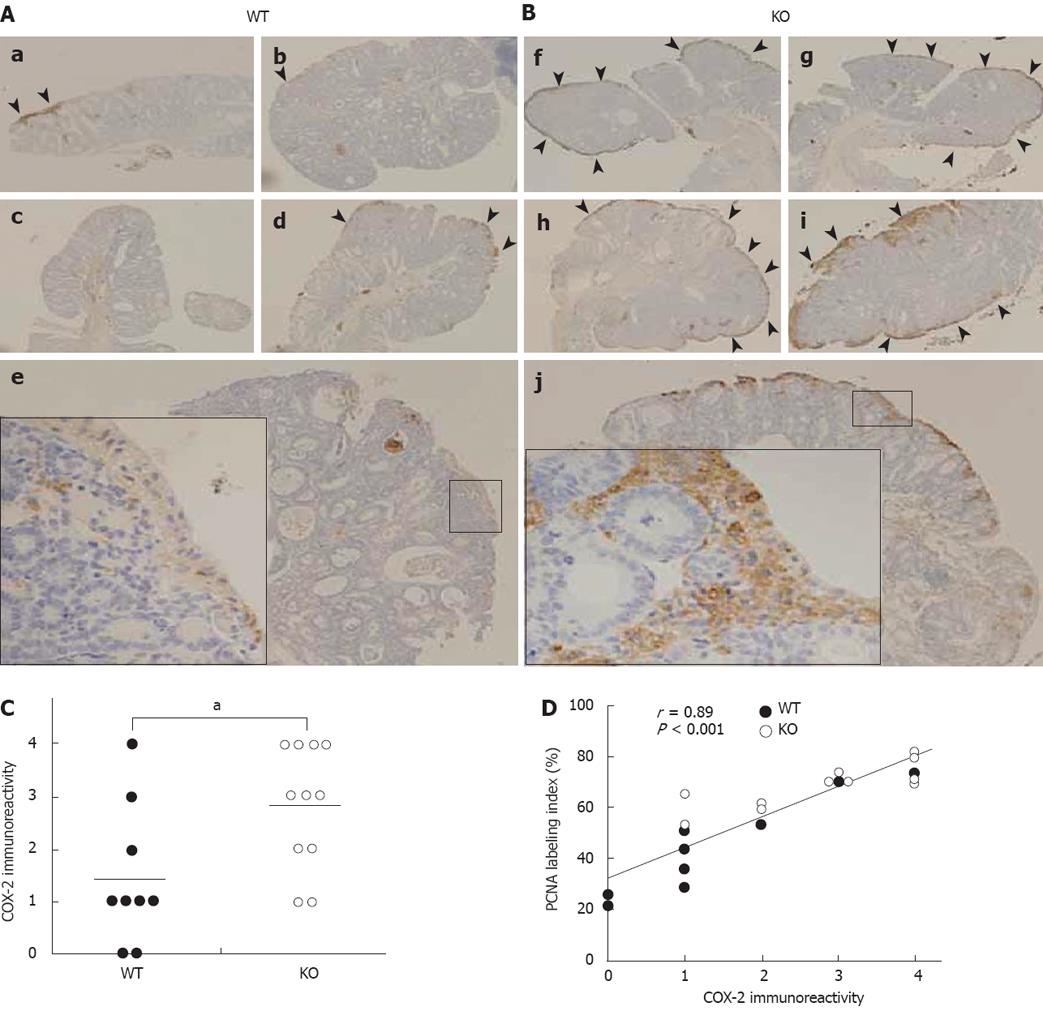
Figure 4 COX-2 overexpression in colorectal tumors of KO mice.
Immunohistochemical staining for COX-2 in colorectal tumors using rabbit anti-mouse COX-2 polyclonal antibody. Immunoreactive COX-2 expression is observed in the epithelium and periluminal stromal cells of the tumors (Arrowheads). A: Representative sections of colorectal tumors in WT mice: e: Boxed area is shown at a higher magnification; B: Representative sections of colorectal tumors in KO mice: j: Boxed area is shown at a higher magnification. Original magnification: × 20 for b, c, d, f, g, h; × 40 for a, e, i, j; × 200 for the boxed area in e and j. C: Statistical analysis of immunoreactive COX-2 expression in colorectal tumors. COX-2 expression was higher in colorectal tumors of KO mice (n = 11) compared with WT mice (n = 9; aP < 0.05, Wilcoxon rank sum test). Horizontal lines: mean value of COX-2 immunoreactivity in colorectal tumors of WT or KO mice. D: Significant correlation between COX-2 immunoreactivity and PCNA-labeling index in colorectal tumors (r = 0.89, P < 0.001, Spearman’s rank correlation). WT mice (n = 9), KO mice (n = 11).
- Citation: Nishihara T, Baba M, Matsuda M, Inoue M, Nishizawa Y, Fukuhara A, Araki H, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Tamura S, Hayashi N, Iishi H, Shimomura I. Adiponectin deficiency enhances colorectal carcinogenesis and liver tumor formation induced by azoxymethane in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(42): 6473-6480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i42/6473.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6473