Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2008; 14(41): 6318-6326
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6318
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6318
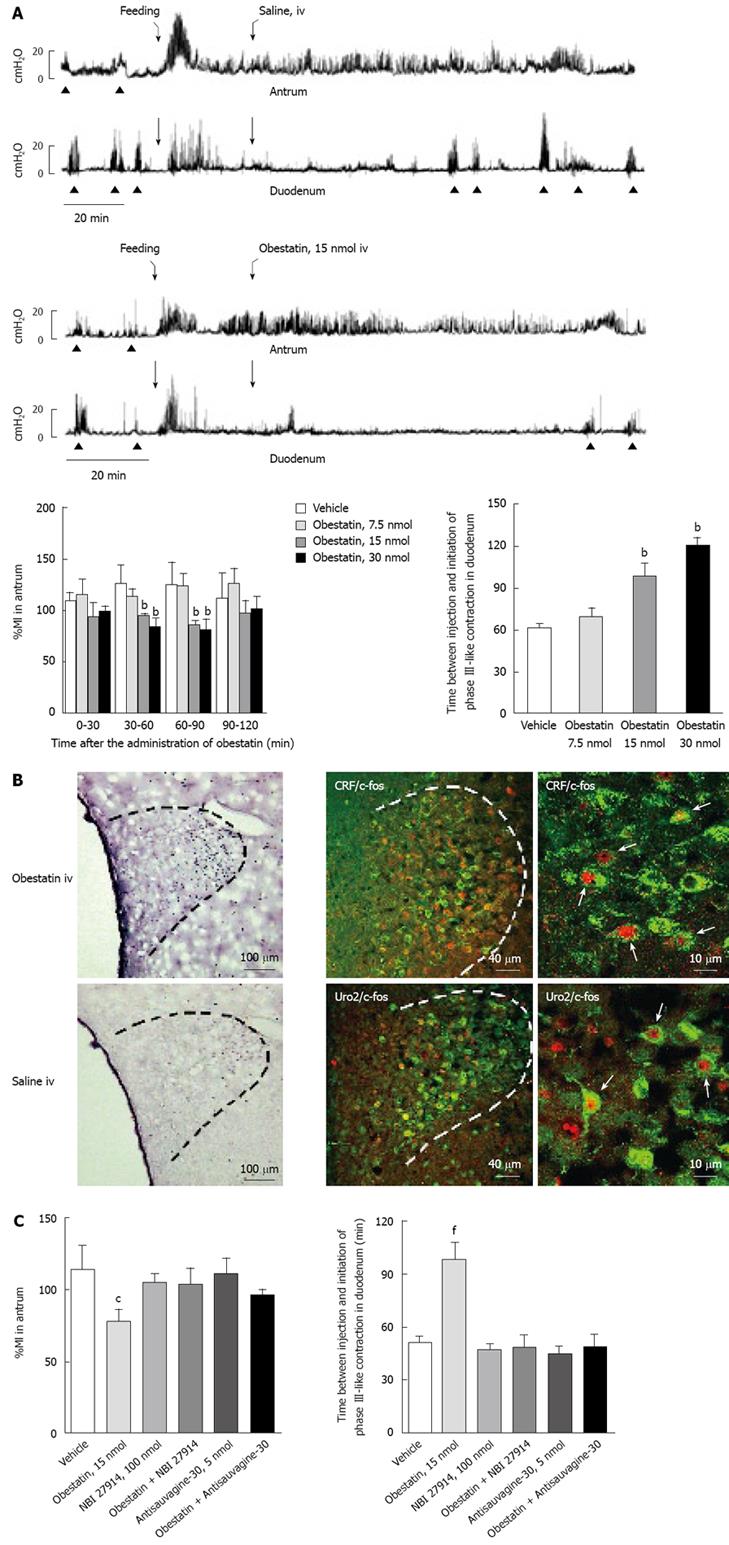
Figure 5 Obestatin and gastroduodenal motility.
A: Effects of iv injection of obestatin on the fed motor activity of the antrum and duodenum. Iv injection of obestatin dose dependently decreases the %MI during the 30-90-min period after injection of obestatin in the antrum, and prolongs the time between the initiation of phase III-like contractions and injection of obestatin in the duodenum. bP < 0.01, compared with vehicle-injected controls; B: The density of c-Fos-positive cells in the PVN is increased by iv injection of obestatin compared to saline-injected control. CRF-positive or urocortin 2-positive neurons are overlapped with c-Fos-positive neurons in the PVN; C: The decrease in %MI that is observed 30-60 min after iv injection of obestatin is reversed by icv injection of the CRF type 1 antagonist NBI-27914 and the CRF type 2 receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30. The elongation of the time between injection of obestatin and initiation of phase III-like contractions in the duodenum induced by iv injection of obestatin is also reversed by icv injection of NBI-27914 and antisauvagine-30. cP < 0.05, fP < 0.01, compared with vehicle-injected controls.
- Citation: Fujimiya M, Asakawa A, Ataka K, Kato I, Inui A. Different effects of ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin on gastroduodenal motility in conscious rats. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(41): 6318-6326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i41/6318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6318