Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2008; 14(40): 6188-6194
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6188
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6188
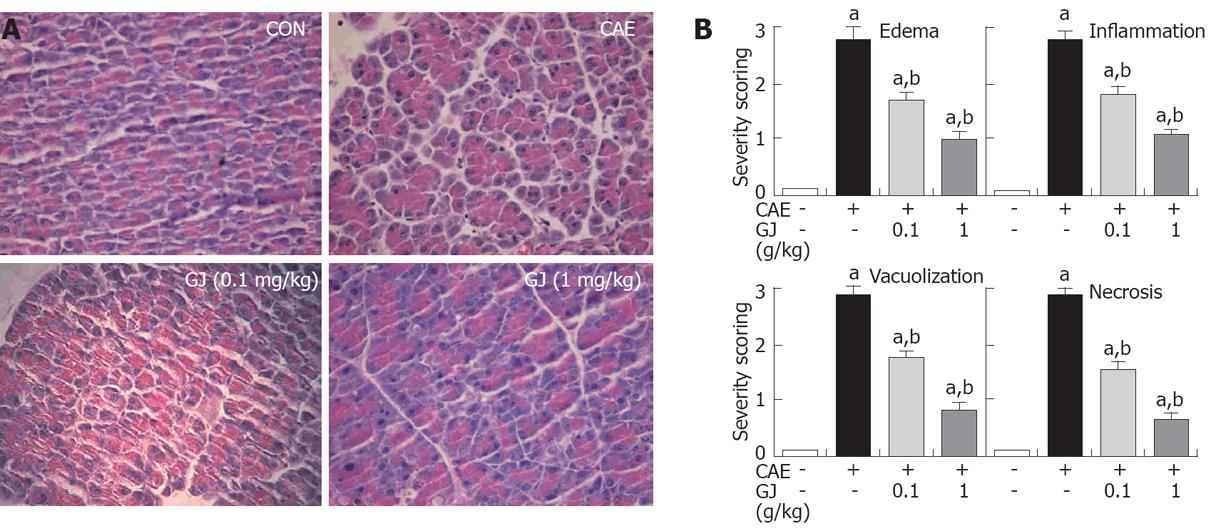
Figure 4 Effects of the GJ on pancreatic inflammatory changes following pancreatitis.
A: Representative H&E-stained sections of pancreas in control mice (CON) who were not given cerulein, in mice given cerulein (CAE), and in mice given GJ (1 mg/kg) at the same time as the first cerulein injection; B: Histological sections of pancreas harvested 12 h after injection of saline (CON), cerulein alone, or GJ (1 or 0.1 mg/kg) given at the same time as the first injection of cerulein. The results were scored from 0 (normal) to 3 (severe) for edema, inflammation, vacuolization, and necrosis. aP < 0.05 vs saline treatment; bP < 0.05 vs cerulein treatment alone. The figure shows the results of one experiment in which 4-5 mice were tested per group. The results obtained were similar to those in three additional experiments (× 200).
-
Citation: Jung WS, Chae YS, Kim DY, Seo SW, Park HJ, Bae GS, Kim TH, Oh HJ, Yun KJ, Park RK, Kim JS, Kim EC, Hwang SY, Park SJ, Song HJ.
Gardenia jasminoides protects against cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(40): 6188-6194 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i40/6188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6188