Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2008; 14(40): 6163-6170
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6163
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6163
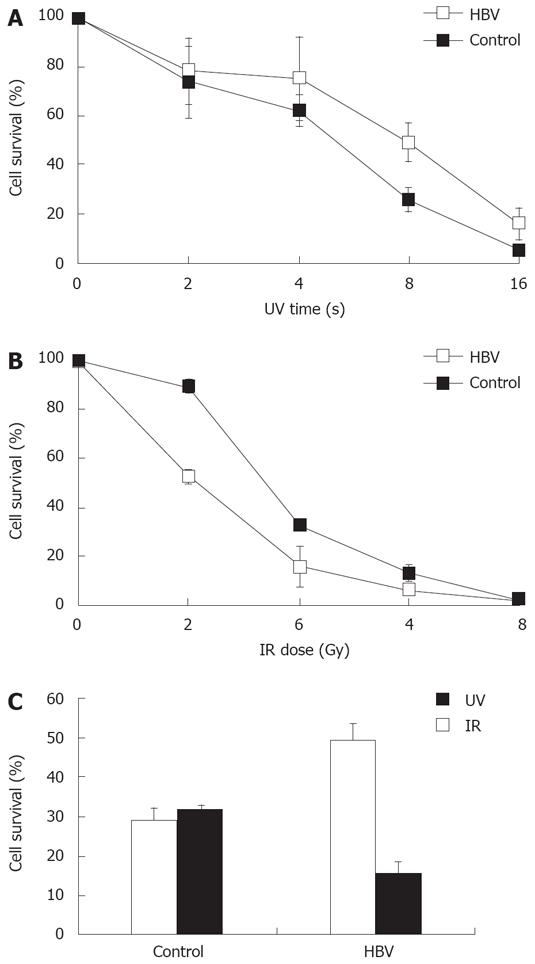
Figure 3 HBV infection hypersensitizes host cells to IR and causes hyper-resistance of host cells to UV.
A: HL7702 cells were treated with indicated doses of IR followed HBV positive serum addition for 24 h, and continued in culture for another 4 d, trypan blue staining was used for viable cell counting; B: HL7702 cells were treated with indicated doses of UV followed by HBV-positive serum addition for 24 h, and continued culture for another 48 h, trypan blue staining was used for viable cell counting; C: HL7702 cells were treated with 8 s of UV or 4 Gy of IR followed HBV infection, and viable cells were counted. Percentage survival was determined by the number of treated cells normalized to untreated cells. Mean and standard error are presented for three independent experiments.
- Citation: Zhao F, Hou NB, Yang XL, He X, Liu Y, Zhang YH, Wei CW, Song T, Li L, Ma QJ, Zhong H. Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated-Rad3-related DNA damage checkpoint signaling pathway triggered by hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(40): 6163-6170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i40/6163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6163