Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2008; 14(40): 6115-6121
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6115
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6115
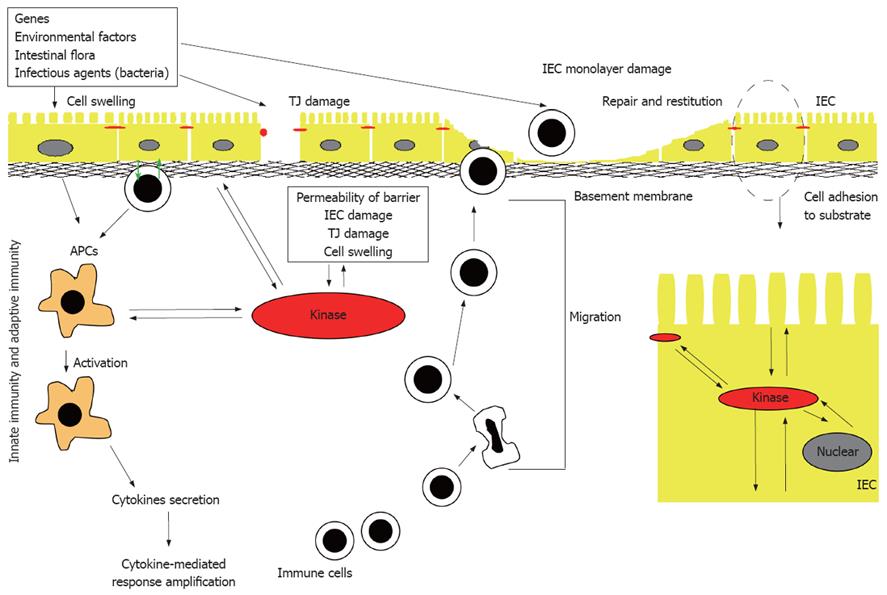
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of IBD.
Many different factors, such as genetic factors, environmental factors, and intestinal non-pathogenic or pathogenic bacteria can damage the mucus, epithelium, or the tight junction, to initiate the inappropriate regulation or deregulation of the immune response, leading to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, decrease in epithelial barrier function and initiation of the inflammation-related signaling pathways. IEC: Intestinal epithelial cell; APC: Antigen presenting cell; TJ: Tight junction.
- Citation: Yan Y, Merlin D. Ste20-related proline/alanine-rich kinase: A novel regulator of intestinal inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(40): 6115-6121
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i40/6115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6115