Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2008; 14(38): 5842-5850
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5842
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5842
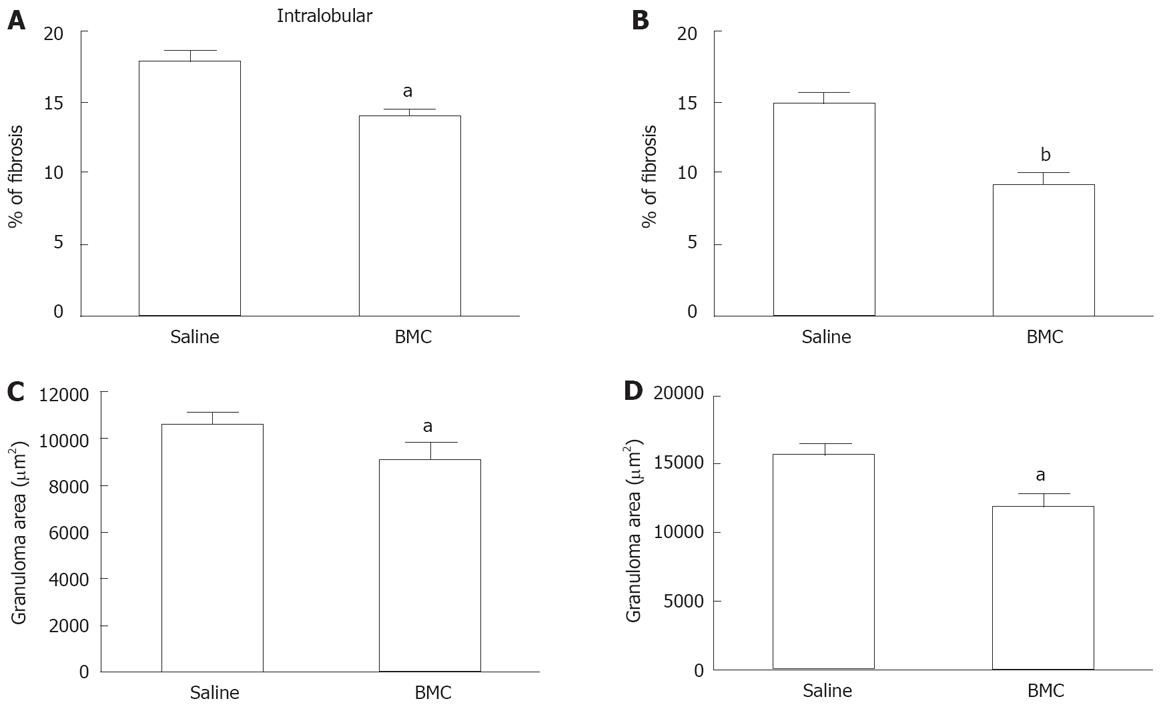
Figure 4 Reduction of fibrosis and granuloma area after BMC therapy.
Mice infected with S.mansoni and treated with saline or BMC by intralobular (A and C) or iv B and D routes were sacrificed 2 mo after treatment. Liver sections sampled randomly and stained with Sirius red-Fast green were examined by optical microscopy. Images were digitalized and analyzed by morphometry. The percentage of fibrosis (A and B) and the area of periocular granulomas (C and D) were evaluated. Data were represented graphically as mean ± SE of 5-14 animals per group. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 compared to saline-treated group.
-
Citation: Oliveira SA, Souza BSF, Guimarães-Ferreira CA, Barreto ES, Souza SC, Freitas LAR, Ribeiro-dos-Santos R, Soares MBP. Therapy with bone marrow cells reduces liver alterations in mice chronically infected by
Schistosoma mansoni . World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(38): 5842-5850 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i38/5842.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5842