Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2008; 14(38): 5797-5809
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5797
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5797
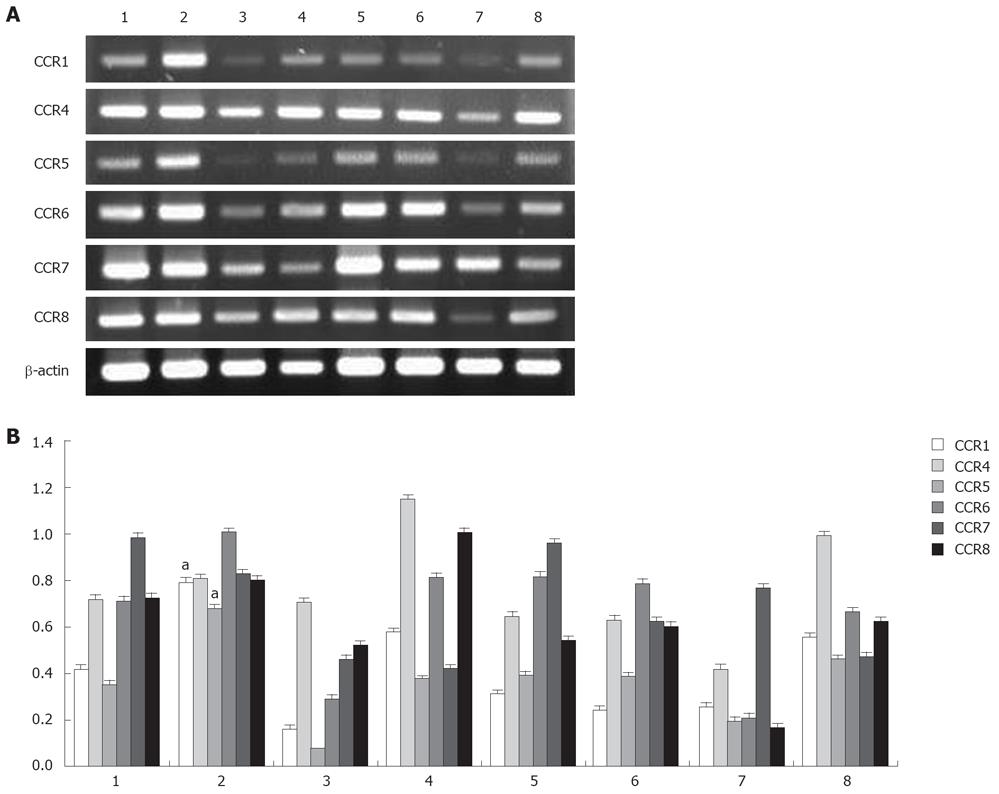
Figure 10 PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcripts in CD4+CD25- and CD4+CD25+ cells (A).
CCR1, CCR4, CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, and β-actin mRNA expression of CD4+CD25- cells (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7) and CD4+CD25+ (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8) in RLNs (lanes 1-4) and PLNs (lanes 5-8) in BaP-only (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6) and control (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8) mice at 32 wk using RT-PCR. Relative expression of chemokine mRNA was compared (B). CD4+CD25+ cells expressed significantly higher levels of CCR1 (a) and CCR5 (a) mRNA. a: P < 0.05
- Citation: Chen YL, Fang JH, Lai MD, Shan YS. Depletion of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells can promote local immunity to suppress tumor growth in benzo[a]pyrene-induced forestomach carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(38): 5797-5809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i38/5797.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5797