Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2008; 14(36): 5570-5583
Published online Sep 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5570
Published online Sep 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5570
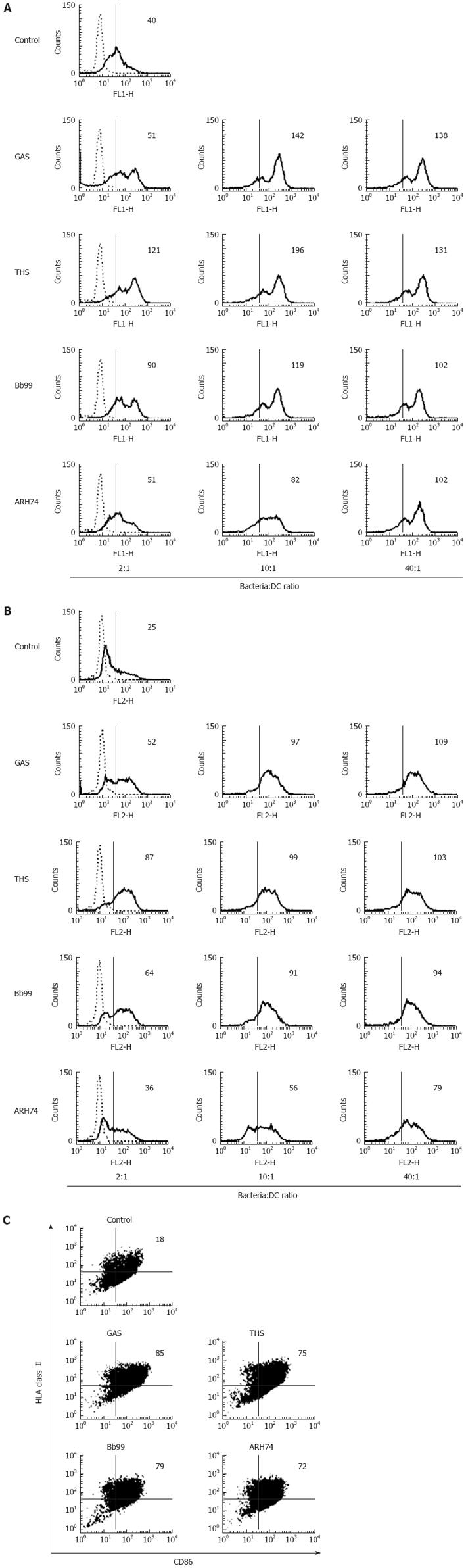
Figure 3 The effect of bacterial dose on the maturation of moDCs.
MoDCs were stimulated with bacteria:host cell ratio of 2:1, 10:1, or 40:1. Cells from four different donors were collected, pooled, and stained with antibodies against (A) HLA class II and (B) CD86. The expression of co-stimulatory molecules was analyzed by flow cytometry. The values represent mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs). Results from a representative experiment out of two are shown. Dotted lines indicate respective isotype controls. The staining profiles of HLA class II/CD86 double-positive (percentages included in the profiles) cells (C). GAS: S. pyogenes; THS: S. thermophilus THS; Bb99: B. breve Bb99; ARH74: L. lactis subsp. cremoris ARH74.
- Citation: Latvala S, Pietilä TE, Veckman V, Kekkonen RA, Tynkkynen S, Korpela R, Julkunen I. Potentially probiotic bacteria induce efficient maturation but differential cytokine production in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(36): 5570-5583
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i36/5570.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5570