Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2008; 14(28): 4473-4479
Published online Jul 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4473
Published online Jul 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4473
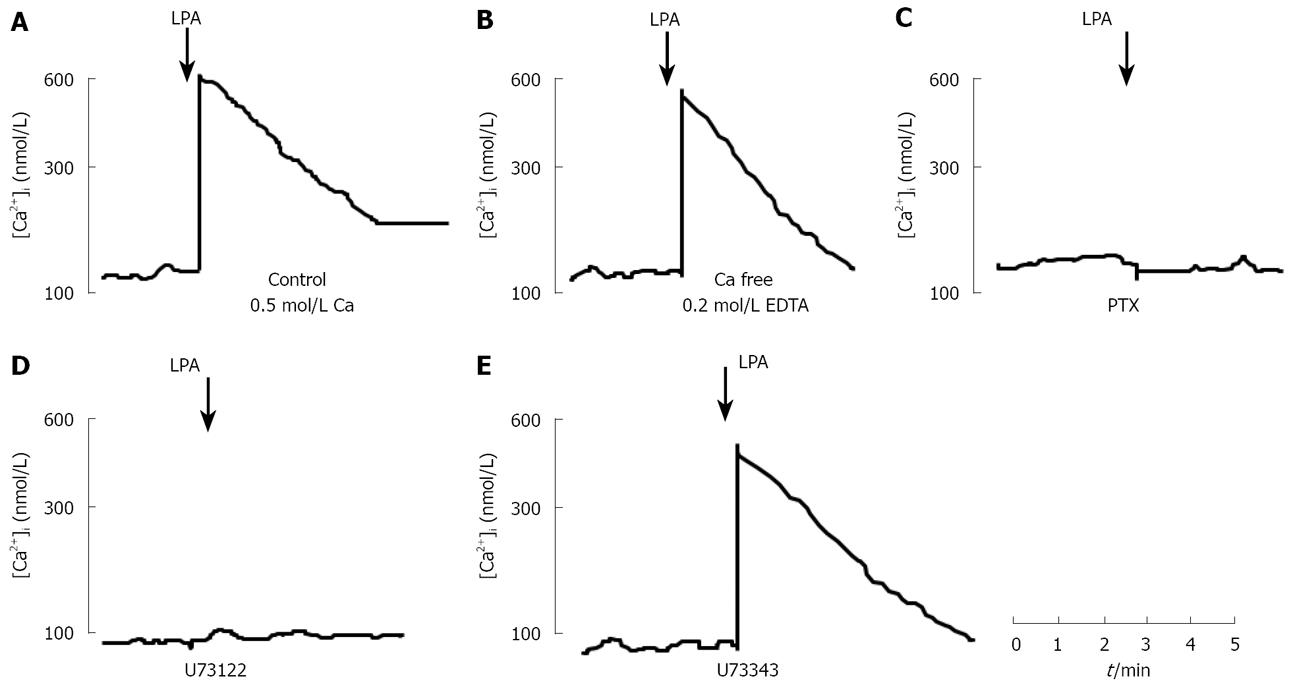
Figure 2 Effect of LPA on cytosolic free calcium concentration [Ca2+]i in Panc-1 cells.
A: Representative Ca2+ signal was evoked by 10 &mgr;mol/L LPA in Panc-1 cells; B: Effect of chelation of extracellular Ca2+ by addition of 0.2 mmol/L EDTA on LPA-induced increases in Ca2+; C: PTX-sensitive effect of LPA on cytosolic free calcium. Panc-1 cells were pretreated with 100 ng/mL of PTX for overnight and loaded with fura-2/AM; D: Effect of U73122, a phospholipase C inhibitor, on LPA-induced increases in cytosolic free calcium in Panc-1 cells. Panc-1 cells were treated with U73122 at a concentration of 10 &mgr;mol/L for 10 min, and then stimulated by 10 &mgr;mol/L LPA; E: Effect of U73343, an inactive analogue of U73122, on LPA-evoked increases in cytosolic free calcium in Panc-1 cells.
- Citation: Arita Y, Ito T, Oono T, Kawabe K, Hisano T, Takayanagi R. Lysophosphatidic acid induced nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB in Panc-1 cells by mobilizing cytosolic free calcium. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(28): 4473-4479
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i28/4473.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4473