Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2008; 14(27): 4324-4331
Published online Jul 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4324
Published online Jul 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4324
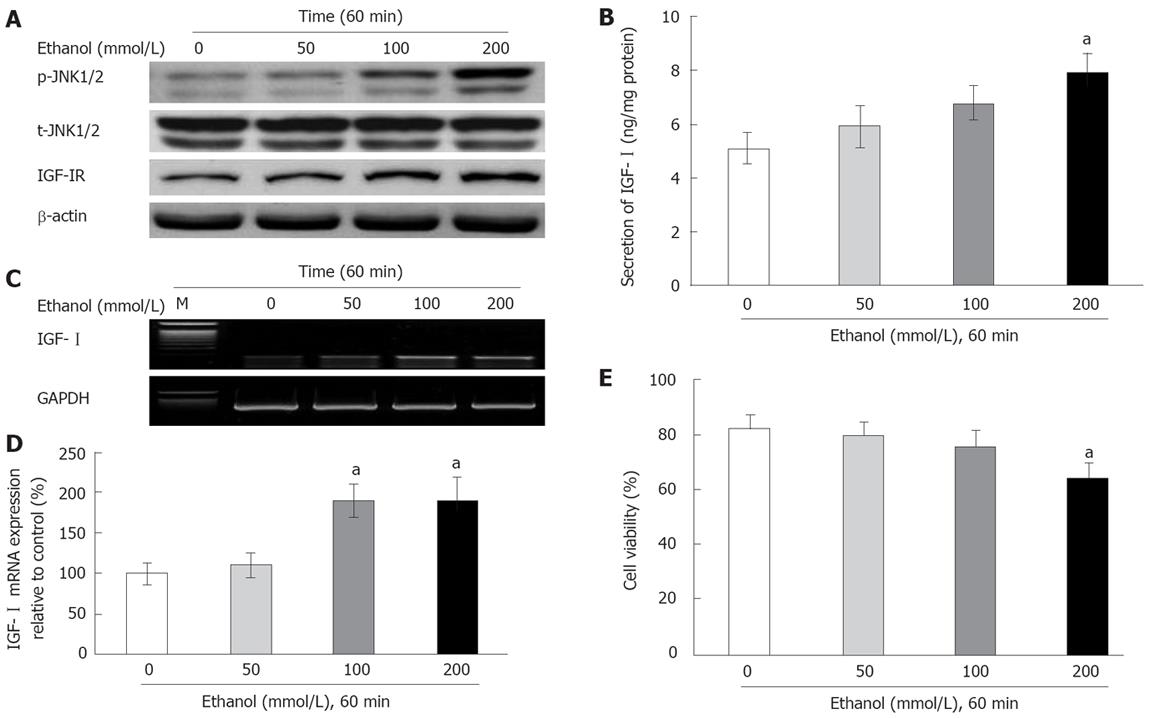
Figure 2 Effects of ethanol on the IGF-I system, JNK1/2 activity, and cell viability at different concentrations (0, 50, 100 and 200 mmol/L) in primary cultured hepatocytes (mean ± SD).
The cells were exposed to ethanol at different concentrations for 60 min. A: P-JNK1/2, t-JNK1/2, and IGF-IR activities; B: IGF-I concentration; C and D: IGF-I mRNA expression; E: Cell viability. β-actin (A) and GAPDH (C) were used as loading controls. The mRNA expression (as indicated by a band at 180 bp, C) was determined by densitometric analysis (D) of the amplification products. Data represent percentages relative to control. The cell viability (D) was determined by the MTT assay. aP < 0.05, vs control (n = 6).
- Citation: Oh YI, Kim JH, Kang CW. Effects of ethanol on insulin-like growth factor-I system in primary cultured rat hepatocytes: Implications of JNK1/2 and alcoholdehydrogenase. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(27): 4324-4331
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i27/4324.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4324